The RF signal detector auto systems are designed to enhance vehicle security and performance by detecting and analyzing radio frequency signals within and around a vehicle. These systems play a crucial role in modern automotive technology by identifying potential threats, ensuring vehicle safety, and improving overall functionality. Integrating intelligent RF signal detectors in automotive technology allows for advanced monitoring of vehicle systems and the detection of unauthorized RF signals. This integration not only helps in preventing theft but also ensures that the vehicle’s electronic systems operate optimally. Safeguard Your Home or Work Area with this RF signal detector auto, perfect for detecting hidden cameras and listening devices. Understanding the role and benefits of RF signal detector auto systems is essential for leveraging their full potential in enhancing automotive security and performance.
How RF Signal Detector Auto Work
An RF (Radio Frequency) Signal Detector is a device used to detect and measure the presence of radio frequency signals in a specific area. These signals can come from various sources, such as wireless networks, mobile phones, or even hidden surveillance equipment. The auto-working feature refers to the device’s ability to automatically scan for and detect RF signals without requiring manual adjustments. Here’s a detailed description of how it works:
Signal Reception
The RF signal detector typically has an antenna or a set of antennas that are designed to capture RF signals within a certain frequency range. These signals can range from a few kilohertz (kHz) to several gigahertz (GHz), depending on the device’s design. The detector’s frequency range usually covers the most common RF bands, such as those used for Wi-Fi (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz), cellular networks (800 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, etc.), Bluetooth, and even signals from microwave ovens or hidden surveillance equipment.
Automatic Scanning
The “auto” feature of an RF signal detector refers to its ability to automatically scan for active radio frequencies. Once powered on, the detector continuously scans the surrounding area for signals. It does this by sweeping through a wide range of frequencies and monitoring for any anomalies or transmissions. This scanning process is often done in real time, allowing the device to detect changes in the signal environment.
- Auto-Scan Functionality: Many detectors have an auto-scan function, where they automatically adjust the scanning process based on the strength of the signals detected. If a signal is found, the device will focus on the specific frequency where the signal is most powerful, narrowing down the range to pinpoint the source more accurately.
Signal Detection and Analysis
Once an RF signal is detected, the detector processes the signal by analyzing its strength, frequency, and sometimes modulation type (e.g., AM, FM, digital). The detector will usually display the results on a screen or through visual or audio indicators.
- Signal Strength: The signal strength is often displayed as a bar graph or numeric value. The stronger the signal, the higher the reading.
- Frequency Identification: Some advanced RF signal detectors can display the exact frequency of the detected signal, allowing users to identify what kind of signal it might be (Wi-Fi, cellular, etc.).
- Modulation Type: Some detectors are sophisticated enough to analyze the modulation type of the signal, which can help differentiate between types of communication (e.g., voice, data, etc.).
Alert Mechanism
Once a signal is detected, an RF signal detector typically alerts the user in one of the following ways:
- Visual Alerts: LED lights or a screen display signal strength, frequency, or other relevant information.
- Audio Alerts: A beeping or a series of tone variations indicate the presence of an RF signal. The frequency of the beep may increase as the signal gets stronger.
- Vibration: In some cases, the device may vibrate to alert the user to the presence of a signal, which is particularly useful in covert or sensitive environments.
Frequency Filtering and Identification
To help narrow down the types of signals, many RF detectors come with filters that allow the user to focus on certain types of signals. For example, users might set the detector to ignore lower-frequency signals (e.g., below 1 GHz) and focus only on higher frequencies typically used by Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. This makes it easier to identify specific sources of interference or unwanted transmissions.
Automatic Adjustment for Sensitivity
Some RF detectors feature auto-sensitivity adjustment, which means that the device can automatically modify its sensitivity based on the detected signal. If a signal is weak, the detector might increase its sensitivity to improve detection. Conversely, if a signal is very strong, it may reduce sensitivity to avoid signal overload and false positives.
Data Logging and Reporting (Optional)
Higher-end RF detectors might include the ability to store detected signal data, including the time, frequency, and signal strength. This data can be useful for analyzing trends or identifying patterns over time, such as identifying the presence of unauthorized RF devices over a period.
An RF Signal Detector with Auto Work functionality is a device that automatically scans for radio frequency signals across a wide frequency range. It detects signals, analyzes their strength, frequency, and sometimes modulation type, and then provides alerts to the user. The “auto” feature refers to the device’s ability to automatically adjust its scanning and sensitivity settings, providing real-time results with minimal manual intervention. This makes it a valuable tool for identifying hidden RF devices, troubleshooting interference, or monitoring RF environments.

RF Signal Detector Auto Frequency Range
The frequency range of an RF (Radio Frequency) signal detector can vary depending on the model and its intended use. Different RF detectors are designed to cover different ranges of frequencies, and the specific frequency range typically indicates the types of signals the detector is capable of identifying. Here’s an overview of the frequency range that an RF signal detector might cover:
Common Frequency Ranges for RF Signal Detectors
- Low Frequency (LF):
- Range: 30 kHz to 300 kHz
- Typically used for industrial applications, power line communications, and some types of radio communications.
- Medium Frequency (MF):
- Range: 300 kHz to 3 MHz
- Used for AM radio broadcasting, maritime communication, and some amateur radio frequencies.
- High Frequency (HF):
- Range: 3 MHz to 30 MHz
- Commonly used for shortwave radio, amateur (ham) radio, and international broadcasting.
- Very High Frequency (VHF):
- Range: 30 MHz to 300 MHz
- Includes TV and FM radio broadcasts, two-way radio communications (police, fire, aviation), and some types of wireless communications (e.g., older cordless phones, wireless microphones).
- Ultra High Frequency (UHF):
- Range: 300 MHz to 3 GHz
- Used by Wi-Fi (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz), Bluetooth, GPS, TV broadcasts, and various wireless communication systems. This is a common frequency range for most consumer electronics and is often found in RF signal detectors for general-purpose applications.
- Super High Frequency (SHF):
- Range: 3 GHz to 30 GHz
- Used for radar, satellite communication, some microwave links, and high-speed wireless communication technologies (e.g., some Wi-Fi routers, 5G technologies).
- Extremely High Frequency (EHF):
- Range: 30 GHz to 300 GHz
- Used in advanced radar systems, satellite communications, and experimental wireless technologies.
Typical RF Signal Detector Frequency Range
Most general-purpose RF signal detectors designed for consumer or professional use will cover a range that includes VHF, UHF, and sometimes SHF, with a focus on the most commonly used frequencies. For example:
- VHF (30 MHz to 300 MHz): This covers a wide range of wireless communications, including FM radio, television signals, and two-way radios.
- UHF (300 MHz to 3 GHz): This range is critical for many wireless technologies, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and certain cellular frequencies.
- SHF (3 GHz to 30 GHz): Higher-end models may cover part or all of this range, especially if the detector is designed to detect signals from microwave sources, satellite systems, or newer 5G networks.
Example of Frequency Range in RF Signal Detectors
- Entry-level detectors: These may have a frequency range of 1 MHz to 6 GHz, covering everything from AM radio up to certain Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and mobile phone frequencies.
- Mid-range detectors: These might cover 10 MHz to 8 GHz or 30 MHz to 12 GHz, providing more comprehensive coverage across different communication technologies.
- High-end detectors: Advanced models could cover 10 MHz to 24 GHz or even the full 30 MHz to 40 GHz range, capable of detecting a broader spectrum of RF signals including newer 5G, satellite, and radar frequencies.
Auto Frequency Scanning
RF detectors with auto frequency scanning will automatically scan across a set range of frequencies. The detector will typically be pre-configured to scan across a wide spectrum (e.g., 1 MHz to 6 GHz or 30 MHz to 3 GHz), and the device will adjust sensitivity to find the strongest signals in that range. Some models also allow users to define specific frequency ranges to scan within, optimizing detection for particular sources of interference or unauthorized transmissions.
Factors Affecting Frequency Range
- Device Type: Consumer-grade RF detectors often focus on VHF and UHF, whereas professional-grade detectors may extend into higher frequencies like SHF and EHF.
- Application: Detectors designed for specific purposes (e.g., for detecting Wi-Fi or cellular signals) may be tuned to specific frequency bands.
- Price and Quality: Higher-end models with more advanced features tend to have a wider frequency range and more precise scanning capabilities.
An RF signal detector’s frequency range can be as broad as 1 MHz to 40 GHz, depending on the model. Most general-purpose devices cover the VHF (30 MHz to 300 MHz) and UHF (300 MHz to 3 GHz) ranges, and some may include SHF (3 GHz to 30 GHz) for higher-frequency communications. The auto frequency scanning feature allows the detector to automatically search through a range of frequencies to identify RF signals without requiring manual tuning, making the process efficient and convenient.

Calculate RF Signal Detector Auto Working Distance
The auto working distance of an RF signal detector refers to the maximum range at which it can effectively detect radio frequency (RF) signals. This distance depends on several factors, including the strength of the signal, the sensitivity of the detector, environmental conditions, and the type of signal being detected.
Key Factors Affecting the Working Distance
- Signal Strength:
- Stronger signals (e.g., from a high-powered transmitter) can be detected from farther away, while weaker signals (e.g., from low-power devices) may require the detector to be closer.
- Detector Sensitivity:
- The sensitivity of the RF signal detector plays a significant role. A more sensitive detector can detect weaker signals at greater distances. Sensitivity is usually specified in terms of the detector’s minimum detectable signal strength, such as dBm (decibels milliwatts).
- Frequency of the Signal:
- Lower frequencies (e.g., VHF and UHF) tend to travel longer distances and penetrate obstacles better than higher frequencies (e.g., SHF or EHF), which have a more limited range due to higher attenuation.
- Power of the Signal Source:
- A high-powered RF transmitter (e.g., a cellular tower or satellite) can be detected at much greater distances compared to a low-powered device (e.g., a Bluetooth device or a Wi-Fi router).
- Environmental Conditions:
- Physical obstructions like walls, buildings, or terrain can attenuate or block RF signals, reducing detection distance. Open areas without interference allow for greater detection ranges.
- Type of Antenna:
- The type of antenna used by both the RF signal detector and the signal source influences the range. Directional antennas generally provide longer detection distances compared to omnidirectional antennas.
General RF Signal Detector Working Distance Estimates
- Low-power devices (e.g., Bluetooth, Wi-Fi):
- Distance: 10 meters to 100 meters (depending on signal strength and detector sensitivity).
- These signals are often relatively weak and are subject to interference from obstacles.
- Cellular and Wi-Fi signals (mid-range frequencies, moderate power):
- Distance: 100 meters to 1 km.
- Depending on the power of the signal, an RF signal detector might detect signals from mobile phones or Wi-Fi routers at distances ranging from tens to hundreds of meters.
- High-power sources (e.g., radio towers, satellite signals):
- Distance: 10 km to 100+ km.
- For powerful signals, like those from radio towers or satellite communications, detectors can work over large distances, especially in open areas with minimal interference.
- Radar and military-grade signals (very high power, specialized equipment):
- Distance: 100 km or more.
- Military or high-powered radar signals can be detected from distances over 100 kilometers, especially if the detector is designed to handle such high-energy transmissions.
Example Calculation
If you’re trying to calculate the distance at which an RF signal detector can detect a signal, a simplified approach involves the Friis Transmission Equation, which calculates signal strength based on distance and other variables. A typical version of the equation for free space is:
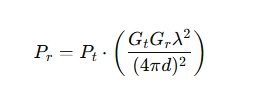
Where:
- Pr = received power
- Pt = transmitted power
- Gt and Gr = gains of the transmitting and receiving antennas
- λ = wavelength of the signal
- d = distance between the transmitter and receiver
To calculate the maximum working distance, you would need to know the transmitted power, antenna gains, and frequency of the RF signal
The auto working distance of an RF signal detector varies widely based on factors like signal strength, frequency, environmental conditions, and the type of equipment. In general, consumer-grade RF detectors can detect signals up to a few hundred meters for Wi-Fi or cellular signals, while specialized detectors designed for high-power or long-range signals can work over several kilometers or more.

RF Signal Detector Auto: Benefits of RF Signal Detectors in Vehicles
RF signal detectors have become increasingly valuable tools for enhancing vehicle security and functionality. Here are twelve benefits of incorporating RF signal detectors into automotive systems:
How RF Signal Detectors Enhance Vehicle Security
- Detection of Unauthorized Tracking Devices: An RF signal detector auto helps identify hidden tracking devices that might be attached to the vehicle. This is particularly useful for preventing unauthorized tracking and monitoring of the vehicle’s location.
- Prevention of Remote Keyless Entry Hacking: RF signal detectors can detect signals from potential hackers attempting to intercept or replicate the signals used by remote keyless entry systems. By identifying these signals, vehicle owners can take preventive measures.
- Detection of Spy Cameras: In the event of suspected surveillance or privacy breaches, an RF signal detector auto can identify and locate hidden cameras that emit RF signals, thereby protecting the vehicle’s occupants from unwanted surveillance.
- Identification of Wireless Intrusions: Modern vehicles often feature wireless communication systems, making them vulnerable to interference or intrusion. An RF signal detector can identify unauthorized or suspicious RF signals that might indicate potential security threats.
- Enhanced Personal Privacy: By using an RF signal detector auto, vehicle owners can ensure that their personal data and communications remain secure from unauthorized RF signal interception.
- Protection Against Signal Jamming: Some RF signal detectors are designed to detect jamming attempts that could disrupt critical vehicle systems, such as GPS navigation and communication systems, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
- Monitoring of In-Car Electronics: An RF signal detector auto can help in monitoring and detecting any unauthorized or malfunctioning electronic devices within the vehicle that might affect performance or safety.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that your vehicle is equipped with an RF signal detector can provide peace of mind by offering an additional layer of security and helping to identify potential security issues before they escalate.
Applications of RF Signal Detectors in Modern Automotive Systems
- GPS Signal Monitoring: Many vehicles use GPS for navigation and tracking. RF signal detectors help monitor the integrity of GPS signals and detect any potential interference or unauthorized tracking.
- Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Security: RF signal detectors can identify unauthorized Bluetooth or Wi-Fi devices within the vehicle, ensuring that only approved devices are connected and preventing potential security breaches.
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): RF signal detectors can be used to monitor the RF signals related to ADAS components, such as radar and lidar sensors, ensuring they are functioning correctly and not being tampered with.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication: In modern vehicles equipped with V2X communication systems, RF signal detectors help in ensuring that these communications are secure and free from interference or unauthorized access.
- Remote Diagnostics and Updates: RF scanner signal detectors can help monitor signals related to remote diagnostic systems and over-the-air updates, ensuring that these processes are secure and free from tampering.
- In-Car Entertainment Systems: For vehicles equipped with advanced in-car entertainment systems, RF signal detectors can ensure that all wireless communications within the system are secure and functioning as intended.
- Key Fob Security: RF signal detectors can help in monitoring the signals emitted by key fobs, ensuring that they are not being duplicated or intercepted by unauthorized individuals.
- Emergency Response Systems: In vehicles equipped with emergency response systems, RF signal detectors can help ensure that signals related to emergency calls are transmitted without interference.
How to use rf signal detector:
Power On: Turn on the RF detector by pressing the power button or switching it on.
Select Frequency Range (if available): Choose the frequency band or sensitivity level to match the type of signal you are detecting (e.g., wireless cameras, GPS trackers, audio bugs).
Scan the Area: Move the detector slowly around the area you want to check. Pay special attention to objects where bugs may be hidden, such as electronics, light fixtures, or furniture.
Monitor the Signal Strength: Watch the signal strength meter or listen for audible beeps. A rising signal level or faster beeping indicates you are getting closer to the source.
Pinpoint the Source: Adjust sensitivity if needed—reduce it to narrow down the exact location when close to a signal. Some detectors may also allow you to switch between vibration or sound modes to make pinpointing easier.
Check for False Alarms: Turn off nearby Wi-Fi devices or known RF sources to avoid interference or false readings.
Repeat if Necessary: Rescan the area to ensure no other suspicious signals are present.
Unveiling the Most Accurate RF Signal Detector Models
RF Signal Detector Auto: RF Signal Detector App Integration
RF Signal Detector Auto apps have revolutionized the way automotive enthusiasts and security professionals monitor and manage RF signals in vehicles. Here’s an overview of RF signal detector apps designed specifically for automotive use:
RF Signal Detector Apps for Automotive Use
RF signal detector apps provide users with the ability to monitor and analyze RF signals using their smartphones or tablets. These apps leverage the device’s hardware to detect RF emissions and provide real-time data on signal strength, frequency, and potential sources. Integrated with modern automotive systems, these apps enhance vehicle security and performance monitoring by offering a convenient and accessible means of signal detection.
Features and Functionalities of RF Signal Detector Apps for Vehicles
Features:
- Real-Time Signal Detection: Provides real-time monitoring of RF signals, allowing users to instantly identify and respond to potential security threats or system malfunctions.
- Frequency Analysis: Enables detailed analysis of detected frequencies, helping users distinguish between different types of RF signals and identify their sources.
- Signal Strength Meter: Displays the strength of detected RF signals, aiding in the localization of signal sources and the assessment of signal quality.
- Customizable Alerts: Users can set up customizable alerts for specific signal types or strengths, ensuring that they are notified of potential issues as they arise.
- Signal Logging: Records detected signals over time, allowing users to review historical data and identify patterns or trends related to RF signal activity.
- Graphical Display: Provides visual representations of signal data through graphs and charts, making it easier to analyze and interpret RF signal information.
- Integration with Vehicle Systems: Some apps can integrate with vehicle systems to provide enhanced monitoring and control over automotive RF communications.
- User-Friendly Interface: Designed with intuitive interfaces, these apps make it easy for users to navigate and operate the signal detection features effectively.
Functionalities:
- Detection of Unauthorized RF Devices: Identifies and locates unauthorized RF devices within the vehicle, enhancing security and preventing potential tampering.
- Monitoring of In-Car Communications: Monitors RF signals related to in-car communication systems, ensuring that they are functioning correctly and securely.
- GPS Signal Verification: Verifies the integrity of GPS signals and identifies potential sources of interference or unauthorized tracking.
- Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Security: Monitors Bluetooth and Wi-Fi signals for unauthorized connections, enhancing the security of in-car wireless communications.
- Signal Interference Identification: Detects and analyzes sources of RF signal interference that may affect the performance of automotive systems.
- Vehicle Diagnostics: Assists in diagnosing issues related to RF communication systems within the vehicle, providing valuable insights for troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Emergency Signal Monitoring: Monitors signals related to emergency response systems, ensuring that they are transmitted without interference.
- Customizable Signal Profiles: Allows users to create and manage profiles for different types of RF signals, facilitating more targeted monitoring and analysis.
RF Signal Detector Auto: Professional RF Signal Detector for Automotive Use
Professional RF Signal Detector Auto are essential tools for advanced automotive applications, offering a range of features and benefits tailored to meet the needs of automotive professionals and enthusiasts. Here’s a detailed look at the characteristics and benefits of using high-end RF signal detectors in vehicles:
Characteristics of Professional RF Signal Detectors Suitable for Automotive Applications
- Broad Frequency Range: Professional RF signal detectors typically cover a wide range of frequencies, allowing them to detect various RF signals used in automotive systems, including GPS, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi.
- High Sensitivity: Equipped with high-sensitivity sensors, these detectors can accurately detect weak or low-level RF signals, providing precise readings and reliable performance.
- Advanced Signal Processing: Features advanced signal processing capabilities that enhance the accuracy of signal detection and analysis, filtering out noise and improving signal clarity.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Provides real-time monitoring of RF signals, enabling users to instantly identify and address potential issues or security threats.
- Detailed Data Reporting: Offers comprehensive data reporting, including signal strength, frequency, and source identification, facilitating in-depth analysis and troubleshooting.
- Durable Construction: Designed with rugged and durable materials to withstand the demands of automotive environments, ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
- User-Friendly Interface: Equipped with intuitive interfaces and controls that make it easy for users to operate and navigate the detector’s features.
- Integration Capabilities: Capable of integrating with automotive systems and other diagnostic tools, providing a cohesive solution for monitoring and managing RF signals in vehicles.
8 Benefits of Using High-End RF Signal Detectors in Vehicles
- Enhanced Security: High-end RF signal detectors offer advanced security features that help identify and prevent unauthorized tracking or surveillance of the vehicle.
- Improved Accuracy: Provides precise and accurate detection of RF signals, ensuring reliable performance and effective monitoring of automotive systems.
- Comprehensive Signal Analysis: Offers detailed analysis of RF signals, including frequency and strength measurements, helping users diagnose and address complex issues.
- Advanced Features: Equipped with advanced features such as real-time monitoring, signal logging, and customizable alerts, enhancing the overall functionality of the detector.
- Reliable Performance: Built with high-quality components and durable construction, ensuring consistent and reliable performance in various automotive environments.
- Efficient Troubleshooting: Facilitates efficient troubleshooting of automotive RF communication systems by providing detailed data and insights into signal performance.
- Enhanced Vehicle Integration: Integrates seamlessly with automotive systems, allowing for comprehensive monitoring and management of RF signals across different vehicle components.
- Increased Peace of Mind: Offers greater peace of mind by ensuring that RF communications within the vehicle are secure and free from interference or unauthorized access.
Top RF Signal Detector NZ Reviews: Find the Best Choices
RF Signal Detector Auto: RF Signal Detector Circuit in Automotive Systems
RF Signal Detector Auto circuits play a crucial role in modern automotive systems, offering essential functions that enhance vehicle performance and security. Here’s a comprehensive overview of their role and integration into vehicle systems:
Explanation of RF Signal Detector Circuits and Their Role in Automotive Applications
RF signal detector circuits are specialized electronic systems designed to detect and analyze radio frequency signals. In automotive applications, these circuits are pivotal for several functions:
- Signal Monitoring: RF signal detector circuits continuously monitor the RF environment within the vehicle. This includes detecting signals from GPS, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and other wireless communication systems. However, it’s essential to note that RF signal detector false positives can occur, potentially leading to alerts from harmless signals like nearby cell phones or Bluetooth devices. Proper calibration and filtering of these circuits are necessary to minimize false positives and ensure accurate threat detection.
- Security Enhancement: One of the primary roles of RF signal detector circuits is to enhance vehicle security. These circuits can detect unauthorized RF signals that may indicate attempts to track or interfere with the vehicle’s communication systems. By identifying such signals, vehicle owners can take preventive actions to secure their vehicle.
- Interference Detection: RF signal detector circuits are essential for identifying and mitigating interference from other electronic devices. In automotive systems, interference can affect the performance of critical components like GPS navigation, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and communication modules. Detecting and addressing interference ensures that these systems operate reliably.
- Diagnostic Capabilities: These circuits are valuable for diagnosing issues related to RF communications within the vehicle. By analyzing the RF signals, technicians can pinpoint malfunctions or irregularities in systems that rely on wireless communication, facilitating more efficient repairs and maintenance.
- Regulatory Compliance: RF signal detector circuits help ensure that the vehicle’s communication systems comply with regulatory standards. By monitoring RF emissions and signal characteristics, these circuits contribute to meeting legal requirements related to radio frequency emissions and interference.
How RF Signal Detector Circuits Are Integrated into Vehicle Systems
RF signal detector circuits are integrated into various automotive systems through a combination of hardware and software components. Here’s how this integration typically works:
- Integration with Vehicle Control Units: RF signal detector circuits are often connected to the vehicle’s central control units, such as the engine control module (ECM) or the body control module (BCM). This integration allows for centralized monitoring and management of RF signals across different systems within the vehicle.
- Connection to Communication Modules: These circuits are linked with communication modules that handle different types of wireless communication, including GPS, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi. The RF signal detector circuits continuously monitor signals from these modules, ensuring their proper function and detecting any anomalies.
- Placement and Calibration: Proper placement and calibration of RF signal detector circuits are crucial for accurate signal detection. These circuits are typically installed in locations where they can effectively monitor relevant RF signals without interference from other electronic components. Calibration ensures that the circuits provide precise and reliable data.
- Software Integration: The data collected by RF signal detector circuits is processed and analyzed using specialized software. This software can be integrated with the vehicle’s infotainment system or diagnostic tools, providing users with real-time information on RF signal performance and potential issues.
- User Interfaces and Alerts: RF signal detector circuits often come with user interfaces that display signal information and alerts. These interfaces can be part of the vehicle’s dashboard or integrated into a mobile app, allowing users to monitor RF signals and receive notifications about any detected issues.
- Customization and Upgrades: Modern vehicles may allow for customization and upgrades of RF signal detector circuits. This means that users can adjust settings or enhance the capabilities of the circuits to better suit their specific needs or to integrate with new technologies.
By integrating RF signal detector circuits into automotive systems, vehicles benefit from enhanced security, improved performance, and better diagnostic capabilities. This integration ensures that RF communication systems operate reliably and that any potential issues are promptly addressed.
RF Signal Detector Auto: RF Signal Detector Online Purchasing
Purchasing an RF Signal Detector Auto use online offers convenience and access to a wide range of options. Here’s a guide on how to find and purchase these detectors online, along with tips for selecting reliable sources:
How to Find and Purchase RF Signal Detectors for Automotive Use Online
- Research Available Models: Start by researching different RF signal detector models that are suitable for automotive use. Look for detectors that offer features such as wide frequency range, high sensitivity, and advanced signal processing. Online reviews and product descriptions can provide valuable insights into the performance and suitability of various models.
- Compare Features and Prices: Once you have a shortlist of potential models, compare their features and prices. Pay attention to specifications such as frequency coverage, sensitivity, and additional functionalities. Comparing prices across different online platforms can help you find the best deal.
- Check Seller Reputation: When purchasing online, it’s important to buy from reputable sellers. Look for established e-commerce platforms or specialized automotive electronics retailers with positive reviews and a history of reliable service.
- Verify Product Authenticity: Ensure that the RF signal detector you are purchasing is genuine and not a counterfeit. Check for authenticity guarantees, manufacturer warranties, and product certifications. Reliable sellers will provide clear information about the authenticity of their products.
- Read Customer Reviews: Customer reviews can offer valuable feedback on the performance and reliability of RF signal detectors. Look for reviews from other automotive users who have purchased and used the detectors to get an idea of their effectiveness and potential issues.
- Consider Return Policies: Check the return policies of the online seller before making a purchase. A good return policy allows you to return or exchange the product if it does not meet your expectations or if there are any issues with the detector.
10 Tips for Selecting Reliable Online Sources for RF Signal Detector Purchases
- Look for Specialized Retailers: Choose online sources that specialize in automotive electronics or RF signal detection equipment. Specialized retailers are more likely to offer high-quality products and expert advice.
- Check Seller Ratings: Review the ratings and feedback of the online seller to ensure they have a good reputation for customer service and product quality.
- Verify Contact Information: Ensure that the online seller provides clear contact information, including a physical address and customer support details. This can be helpful in case you need assistance with your purchase.
- Read Product Descriptions Carefully: Thoroughly read the product descriptions to understand the features, specifications, and compatibility of the RF signal detector. This helps in making an informed decision.
- Compare Shipping Options: Check the shipping options and delivery times offered by the seller. Choose a seller that provides reliable shipping services and reasonable delivery times.
- Look for Secure Payment Methods: Ensure that the online seller offers secure payment methods to protect your financial information. Look for payment options such as credit cards or secure payment gateways.
- Check for Manufacturer Support: Verify that the seller provides manufacturer support or warranties for the RF signal detector. This can be important for addressing any issues or defects.
- Read Return Policies: Review the return policies to understand the conditions under which you can return or exchange the product. A flexible return policy provides peace of mind in case of any issues.
- Look for Detailed Product Information: Choose sellers that provide detailed information about the RF signal detectors, including technical specifications, user manuals, and installation guides.
- Compare Prices Across Platforms: Compare prices for the same model across different online platforms to ensure you are getting the best value for your money.
By following these tips, you can find and purchase a high-quality RF signal detector auto online, ensuring that you get a reliable product that meets your needs.
RF Signal Detector Auto Installation and Setup
Proper installation and setup of RF signal detectors in vehicles are crucial for optimal performance and functionality. Here’s a step-by-step guide to installing and configuring RF signal detectors in vehicles, along with best practices for ensuring successful installation:
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing and Setting Up RF Signal Detectors in Vehicles
- Select the Installation Location: Choose an appropriate location for installing the RF Signal Detector Auto in your vehicle. Ideally, the location should be central and free from obstructions to ensure effective signal monitoring. Common locations include near the dashboard or center console.
- Prepare the Installation Area: Clean the area where the RF signal detector will be installed to ensure a secure and stable mount. Remove any dust, dirt, or debris that might affect the installation.
- Mount the Detector: Securely mount the RF signal detector using the provided mounting hardware or adhesive. Ensure that the detector is firmly attached and positioned to allow for effective signal detection.
- Connect Power Supply: Connect the RF signal detector to the vehicle’s power supply. This may involve connecting to the vehicle’s electrical system or using a dedicated power adapter. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper wiring and connection.
- Install Any Additional Components: If the RF signal detector comes with additional components, such as antennas or external sensors, install them according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure that all components are securely connected and positioned correctly.
- Power On the Detector: Turn on the RF signal detector and check for any initial setup prompts or calibration requirements. Follow the instructions provided to complete the initial setup process.
- Configure Settings: Adjust the settings on the RF signal detector according to your preferences and requirements. This may include configuring frequency ranges, sensitivity levels, and alert settings.
- Test the Installation: Perform a test to ensure that the RF signal detector is functioning correctly. Check for accurate signal detection and ensure that all features are working as expected.
- Fine-Tune Calibration: If necessary, fine-tune the calibration of the RF signal detector to optimize its performance.
FAQs about RF Signal Detector Auto
Yes, RF detectors are effective tools for detecting radio frequency signals, provided they are used correctly and chosen based on their intended application. An RF detector works by identifying and measuring electromagnetic fields in the radio frequency spectrum. These devices can detect a wide range of signals, including those from wireless communication devices, hidden cameras, and other electronic equipment emitting RF signals. The effectiveness of an RF detector depends on its sensitivity, frequency range, and the environment in which it is used. High-quality detectors can provide precise readings and help users locate and identify RF sources with a high degree of accuracy. However, it’s essential to choose an RF detector suited to your specific needs and to understand its limitations to ensure reliable results.
An RF signal detector is a device designed to identify and measure radio frequency signals. Its primary function is to detect the presence of RF signals in the environment, which can be useful for a variety of applications. These detectors can find hidden electronic devices, such as spy cameras or tracking devices, by sensing the RF emissions they produce. Additionally, RF signal detectors are used in troubleshooting and maintaining communication systems to ensure signal integrity and performance. The device typically features a display that indicates signal strength or presence, helping users pinpoint the location and source of RF emissions. Advanced models may offer features such as frequency analysis and signal strength measurements for more detailed assessments.
An RF detector will be set off by any device that emits radio frequency signals. Common sources include wireless communication devices like cell phones, Wi-Fi routers, and Bluetooth devices. Other potential sources are hidden cameras, GPS trackers, and wireless microphones, which emit RF signals to transmit data. Additionally, RF detectors may pick up signals from electronic devices like radios, televisions, and even certain household appliances that operate on RF frequencies. It’s important to note that not all RF signals are necessarily harmful or invasive, but detecting them can be crucial for security and troubleshooting purposes. When using an RF detector, be aware of your surroundings and the various RF sources that might trigger the device.
RF signals are detected through the use of specialized equipment that senses electromagnetic fields in the radio frequency spectrum. An RF signal detector typically consists of an antenna that receives RF signals, a receiver that processes the signals, and a display that provides information about the detected signals. When an RF signal is detected, the antenna captures the electromagnetic waves, and the receiver analyzes their frequency and strength. The detector then displays the information on a screen or through other indicators, such as LEDs or sound alerts. Some advanced RF detectors can also perform frequency analysis to provide detailed information about the signal’s characteristics. By measuring the intensity and frequency of the detected signals, users can locate and identify sources of RF emissions.
RF detectors are generally effective in detecting radio frequency signals, including signals from wireless devices like cell phones, Wi-Fi routers, GPS trackers, or hidden surveillance equipment. They work by scanning the electromagnetic spectrum for signals within certain frequency ranges. However, their effectiveness can vary depending on the type of RF signal being emitted, the detector’s sensitivity, and the environment. Some advanced jamming or stealth technologies may evade detection, while cheaper or older detectors may miss certain signals. RF detectors are typically more useful for identifying sources of interference or unauthorized surveillance.
RF detectors are legal in most countries for personal use, as they can be used to detect interference or unauthorized surveillance. However, their use becomes illegal if they are used to actively interfere with communications, such as jamming signals or tampering with wireless networks. In certain regions, like the United States, using an RF detector to evade law enforcement or interfere with legal communications can lead to legal consequences. Always ensure you’re using the device within the bounds of local laws, especially regarding privacy and the unauthorized interception of communications.
Yes, there are several RF detector apps available for smartphones, primarily for Android and iOS devices. These apps use the phone’s built-in sensors, such as the magnetometer and accelerometer, to detect electromagnetic signals in the radio frequency range. While these apps can detect some RF signals like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, they are typically not as accurate or sensitive as dedicated hardware-based RF detectors. Apps may be useful for casual detection or basic tasks, but for more advanced or precise applications, a standalone RF detector is recommended for better performance.
RF (Radio Frequency) signals are used for wireless communication in a wide range of applications, including broadcasting (AM/FM radio), television transmission, mobile phones, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GPS, satellite communication, radar, and more. RF signals carry information by modulating carrier waves at different frequencies. The data can be anything from audio and video content to internet traffic, positioning data, or sensor information. RF signals are also critical in many industrial and military applications, such as remote sensing, navigation, and security systems.
Yes, law enforcement can detect radar detectors, especially when used in vehicles. Specialized devices called “radar detector detectors” (RDD) are used by police to detect the presence of radar detectors in nearby vehicles. RDDs work by detecting the electromagnetic signals emitted by radar detectors when they are turned on, particularly when they are scanning for radar guns. In some countries, such as the U.S. states of Virginia, Washington D.C., and many provinces in Canada, using radar detectors is illegal, and law enforcement can fine individuals for possessing or using them.
Several materials can block or attenuate RF signals. The most effective are metals, as they act as conductive shields, reflecting or absorbing the electromagnetic waves. Materials like aluminum, copper, and steel are commonly used in Faraday cages to block RF signals completely. Other materials that can block or reduce RF signal strength include concrete, brick, and thick walls, especially when combined with metal reinforcements. Certain fabrics, like those used in RFID-blocking wallets, can also attenuate low-frequency RF signals. The effectiveness of a material depends on its thickness and electrical conductivity.

































