An RF IMSI catcher is a sophisticated surveillance device used to intercept and monitor mobile communications by mimicking legitimate cell towers. It operates by capturing the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) numbers from nearby mobile phones, which can reveal sensitive information about individuals and their communications. RF IMSI catcher is a telephone eavesdropping device used for track and locate all mobile phones that are working and receiving signals. Understanding RF IMSI catchers is crucial for both security professionals and the general public. These devices play a significant role in privacy concerns and legal discussions, as they can potentially infringe on personal privacy and security. Awareness and knowledge of RF IMSI catchers help in developing better detection methods and mitigating risks associated with unauthorized surveillance.
Why Customers Love This Product: Key Details
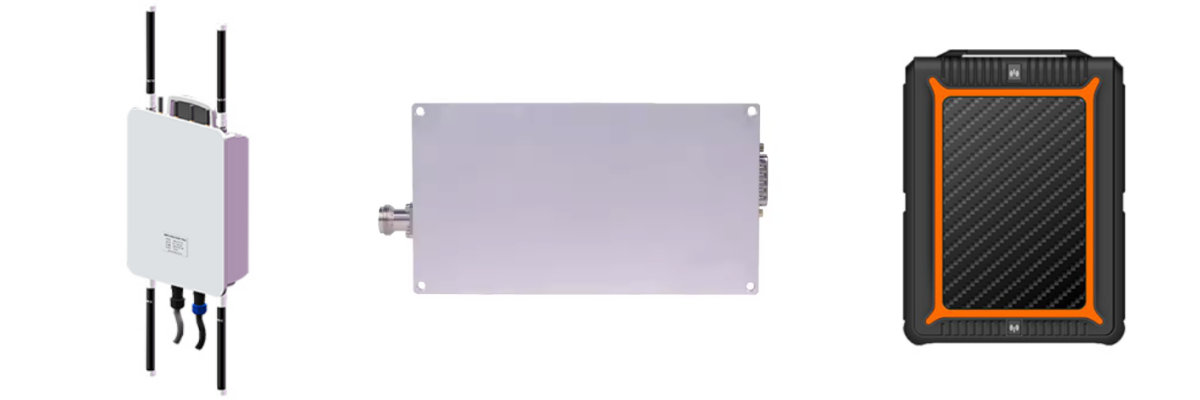

| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Name | RF IMSI Catcher |
| Brand | SZMID |
| Origin | Beijing, China |
| Frequency Range | 2110-2200MHz |
| Output Power | 40±1dBm |
| Gain | 50±1dB |
| Gain Control Range | ≥25dB |
| EVM (Error Vector Magnitude) | ≤3% |
| Passband Ripple | ≤1.5dB |
| Working Temperature | -30~+70℃ |
| Relative Humidity | 5%~95%, no condensation |
| Bandwidth | TDD FDD |
| Application | Communication, IMSI/TMSI/IMEI code detection, mobile signal boosting, Field position collection, mobile signal detection, communication enhancement |
| Features | - Dual band support |
| - Mobile signal amplification | |
| - Compact and reliable operation in extreme environments | |
| - Supports sending messages and call functions (dual band) | |
| - Portable and easy to install |
How RF IMSI Catcher Works
Technical Operation
RF IMSI catchers, also known as cell-site simulators, are sophisticated devices used for intercepting and monitoring mobile communications. These devices operate by mimicking legitimate cell towers, tricking nearby mobile phones into connecting to them. The fundamental purpose of an RF IMSI catcher is to capture International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) numbers from phones in its vicinity. This process involves several technical steps:
- Signal Emission: The RF IMSI catcher emits a signal that mimics the characteristics of a legitimate cell tower. This signal is typically stronger than that of real cell towers in the area, causing nearby phones to connect to it.
- Connection Establishment: Once a phone connects to the RF IMSI catcher, it communicates with the device using standard cellular protocols. During this communication, the IMSI catcher can capture various pieces of information, including the IMSI, which is a unique identifier for the mobile subscriber.
- Data Interception: The RF IMSI catcher can intercept data exchanged between the phone and the legitimate network. This data can include text messages, call details, and other sensitive information depending on the capabilities of the device.
- Signal Processing: After capturing the IMSI and other data, the RF IMSI catcher processes this information. It can use algorithms to extract useful details and sometimes even manipulate the data for further analysis.
- Transmission to Operator: The collected data is transmitted to the operator of the RF IMSI catcher for analysis. This data can be used for tracking the movements of individuals, monitoring communications, or other surveillance purposes.
The technical sophistication of RF IMSI catchers allows them to operate covertly, making detection challenging without specialized equipment.
10 Components and Functionality
- Signal Generator: This component emits the RF signals that mimic a legitimate cell tower. It is crucial for attracting nearby mobile devices.
- Transceiver: The transceiver facilitates bidirectional communication between the RF IMSI catcher and mobile devices, allowing it to capture IMSI numbers and other data.
- Processor: The processor manages the data captured by the device. It decodes and analyzes the signals received from mobile phones.
- Storage Unit: This component stores the captured data, including IMSI numbers, call records, and messages, for later retrieval and analysis.
- Display Interface: The display interface allows the operator to view and manage the collected data in real-time.
- Power Supply: Provides the necessary power for the RF IMSI catcher to operate. It is often designed for long-lasting operation to ensure extended surveillance periods.
- GPS Module: Some advanced RF IMSI catchers include a GPS module to track the location of mobile devices in conjunction with the IMSI data.
- Encryption Module: This component encrypts the data captured by the RF IMSI catcher to protect it from unauthorized access during transmission.
- Cooling System: Ensures that the RF IMSI catcher remains operational by managing heat generated during its operation.
- Software Interface: The software interface allows for the configuration and control of the RF IMSI catcher, including setting parameters for data collection and analysis.
The Complete Guide to RF Signal Detector Rating for Professionals
10 Applications of RF IMSI Catcher
Law Enforcement
- Criminal Investigations: RF IMSI catchers are used in criminal investigations to track suspects and gather evidence. By intercepting IMSI numbers, law enforcement can monitor the movements and communications of individuals under investigation.
- Counter-Terrorism: In counter-terrorism efforts, RF IMSI catchers help in identifying and tracking potential threats. They are used to intercept communications and gather intelligence on terrorist activities.
- Missing Persons: Law enforcement agencies use RF IMSI catchers to locate missing persons by tracking their mobile phone signals. This application is critical in emergency situations where time is of the essence.
- Surveillance Operations: RF IMSI catchers support surveillance operations by providing real-time data on the location and activities of individuals. This data is crucial for monitoring and preventing criminal activities.
- Security Assessments: Law enforcement agencies conduct security assessments using RF IMSI catchers to identify vulnerabilities in communication networks and ensure public safety.
Corporate and Security Uses
- Corporate Espionage Prevention: Businesses use RF IMSI catchers to detect and prevent industrial espionage. By monitoring the communications of employees and competitors, companies can safeguard their intellectual property.
- Data Protection: Corporations employ RF IMSI catchers to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. These devices help in identifying and mitigating security threats related to mobile communications.
- Event Security: During large events, RF IMSI catchers are used to ensure the safety of attendees by monitoring potential security threats and maintaining control over communications.
- Facility Security: Companies use RF IMSI catcher to enhance facility security by detecting unauthorized surveillance devices and ensuring that their premises are secure.
- Compliance Monitoring: Organizations use RF IMSI catchers to ensure compliance with regulations related to data protection and privacy. They help in monitoring communications to prevent breaches and ensure adherence to legal standards.
Portable RF IMSI Catcher Application Scenarios and Uses
A portable RF IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) catcher is a device used to intercept mobile phone signals, primarily to capture IMSI numbers, which are unique identifiers tied to SIM cards within mobile devices. These devices operate by pretending to be legitimate cell towers, thereby enticing mobile phones to connect to them. Once connected, an IMSI catcher can collect the device’s IMSI number, sometimes even gathering location information or intercepting communication, depending on the device’s sophistication. Below are some application scenarios and uses for a portable RF IMSI catcher:
Law Enforcement Surveillance and Monitoring
- Purpose: Used by police and federal agencies, IMSI catchers assist in tracking and monitoring suspects’ mobile devices.
- Application: When deployed in high-crime areas or during investigations, IMSI catchers can collect IMSI data from all nearby devices, aiding in suspect identification. Law enforcement can also track the movement of suspects over time and, in certain cases, intercept communication.
- Advantages: By capturing IMSI numbers from nearby devices, police can narrow down potential suspects, identify criminal networks, and gather real-time data for investigations without direct contact.
Border Security and Immigration Control
- Purpose: Security agencies at borders use IMSI catchers to screen incoming individuals and monitor unauthorized communication channels.
- Application: An IMSI catcher can detect devices as they enter a controlled area, like a border checkpoint, and capture identifying data. This allows security forces to identify travelers and potential threats based on known IMSI data from law enforcement databases.
- Advantages: Provides enhanced security by screening individuals in real-time, potentially identifying persons of interest or detecting suspicious activity across border areas.
Counter-Terrorism and Anti-Drug Operations
- Purpose: Military and intelligence agencies use IMSI catchers in operations where tracking the communication and movement of suspects involved in terrorism or drug trafficking is critical.
- Application: Deployed covertly in high-risk areas or conflict zones, these devices help gather information on targets’ communication networks. They can also help dismantle drug or terror networks by mapping contacts based on IMSI data.
- Advantages: Offers the ability to remotely track key figures in criminal organizations, facilitating targeted interventions and minimizing collateral damage.
Event Security and Crowd Control
- Purpose: During large public events (e.g., concerts, protests, or sports events), security teams use IMSI catchers to ensure safety by monitoring communication and potential threats.
- Application: The device collects IMSI data from the crowd to detect potentially dangerous individuals, based on flagged IMSIs in watchlists. It may also monitor for unauthorized or illegal communication patterns, such as those linked to violence or other criminal activity.
- Advantages: Enables swift response to potential threats in crowded environments, helping organizers maintain event safety and prevent disruptions.
Corporate Security and Confidentiality Enforcement
- Purpose: Corporations use IMSI catchers in restricted or sensitive areas to ensure the security of information and prevent data leaks.
- Application: In areas where confidential data is stored or discussed, companies deploy IMSI catchers to detect unauthorized devices, ensuring no unapproved devices are actively communicating.
- Advantages: Prevents unauthorized access to sensitive areas, monitors devices for confidentiality breaches, and mitigates the risk of corporate espionage.
Research and Analysis in Telecommunications
- Purpose: In controlled environments, researchers may use IMSI catchers to study telecommunications networks and mobile connectivity behavior.
- Application: Researchers capture IMSI data from devices to study signal strength, connectivity issues, or the effectiveness of various cellular network protocols.
- Advantages: Provides valuable insights into network security, performance, and resilience, which can lead to improved network protocols and stronger encryption standards.
Key Considerations and Ethical Concerns
While IMSI catchers are powerful tools, their use raises ethical and legal concerns:
- Privacy Concerns: IMSI catchers capture data from all devices within their range indiscriminately, meaning they can collect data from individuals not involved in any criminal activity.
- Legal Restrictions: The legality of IMSI catcher usage varies by country, with some regions implementing strict regulations due to privacy implications. Unauthorized use may be illegal and subject to strict penalties.
- Data Security: Ensuring collected data is securely handled and stored is crucial to prevent misuse or data breaches.
Portable RF IMSI catchers are versatile devices with broad applications in security, law enforcement, and research. However, responsible and legal use is essential to balancing the benefits of these tools with the privacy rights of individuals.

Identifying RF IMSI Catcher
Identifying an RF IMSI catcher in a given environment can be challenging due to the device’s ability to masquerade as a legitimate cell tower. However, there are a few methods and tools that can be employed to detect and identify the presence of an IMSI catcher:
Anomalous Signal Behavior Detection
- Cell Tower Signal Analysis: IMSI catchers often emit a stronger signal than nearby legitimate cell towers to force devices to connect. This unusual strength or a sudden spike in signal can indicate an IMSI catcher.
- Unusual Network Transitions: Devices may experience frequent or unexpected changes between 2G, 3G, 4G, or 5G, as many IMSI catchers operate on 2G networks due to their weaker encryption protocols.
- Short Cell Tower Lifespan: Legitimate cell towers generally have consistent identifiers over time. If a cell tower identifier suddenly appears, then disappears, it could indicate a portable IMSI catcher.
Mobile Applications for IMSI Catcher Detection
- Apps like SnoopSnitch and AIMSICD: These mobile apps use data from the device to detect and report suspicious cell tower activity, such as unexplained changes in signal or network quality and abnormal location area codes. They can also warn of unexpected tower behavior or security downgrades.
- Limitations: These apps are more effective on rooted or specialized Android devices, as iOS restricts access to the necessary low-level network information, limiting the app’s capability.
Use of Specialized RF Analysis Tools
- Software-Defined Radios (SDR): SDR tools can monitor RF signals and identify unusual broadcast frequencies or suspicious patterns. SDRs capture data on the signal and tower identifier, helping to detect fake cell towers.
- Baseband Analysis Equipment: This equipment analyzes network characteristics in depth, allowing for identification of abnormal network behaviors, like security protocol downgrades, that IMSI catchers may use to gain access to a device.
Monitoring Device Behavior and Battery Usage
- Sudden Battery Drain: If a mobile device frequently connects to an IMSI catcher, it may experience battery drain due to the high level of signaling activity. While this is not a definitive indicator, consistent sudden drains might signal an IMSI catcher presence.
- Unexpected Loss of Encrypted Connections: IMSI catchers may cause devices to lose secure 4G or 5G connections and revert to less secure 2G protocols. This results in a downgrade in connection security, sometimes visible as slower data speeds or an insecure network indicator.
Network Provider and Hardware Solutions
- Network Provider Monitoring: Some network providers monitor for unusual activity in their networks and may alert users to potential IMSI catcher presence, though this capability varies by provider.
- Hardware Detection Devices: Some specialized hardware solutions, designed for corporate or government environments, actively monitor for IMSI catcher devices by continuously analyzing local cellular activity and identifying suspicious connections.
Community Reporting and Collaboration
- Crowdsourced Detection Networks: Platforms that compile data from multiple users, such as AIMSICD’s database, can create a more comprehensive view of potential IMSI catcher locations, allowing communities to alert each other to potential threats.
- Crowdsourced Mobile App Alerts: When a mobile device detects unusual activity through an app, this information can be shared anonymously within a network to increase awareness of potential IMSI catcher locations in high-risk areas.
Limitations of IMSI Catcher Detection
While these methods offer potential ways to detect IMSI catchers, limitations include:
- False Positives: Many IMSI catcher detection methods rely on signal anomalies, which may also be caused by legitimate network issues.
- Limited Device Compatibility: Some methods, like SDR or detection apps, may be limited by the operating system or require advanced technical skills to interpret results accurately.
- Legal and Privacy Considerations: Actively scanning for IMSI catchers may have legal restrictions in certain regions, and privacy considerations should be respected when using or sharing data.
Identifying IMSI catchers remains an evolving area of interest, especially as these devices become more sophisticated. However, using a combination of the above methods can help improve the chances of detecting and mitigating the influence of these devices in sensitive environments.
Multi-frequency RF IMSI Catcher
A multi-frequency RF IMSI catcher is an advanced type of IMSI catcher capable of operating across multiple frequency bands, allowing it to interact with devices on various cellular networks (e.g., 2G, 3G, 4G, and even 5G). This capability enhances the device’s effectiveness by expanding its reach to more mobile devices and reducing the chance of detection due to network-switching inconsistencies.
Key Features and Capabilities of Multi-Frequency RF IMSI Catchers
Multi-Band Connectivity:
- Operates on various frequency bands (e.g., GSM, CDMA, UMTS, LTE, NR), enabling compatibility with multiple generations of mobile technology.
- Can seamlessly target devices regardless of the network generation they are currently using, making it more versatile in heterogeneous cellular environments.
Protocol Downgrade Capabilities:
- Some multi-frequency IMSI catchers can force devices to downgrade from higher-security networks (e.g., 4G, 5G) to lower-security networks (e.g., 2G) to bypass newer encryption and security features.
- Downgrading forces devices into networks with weaker encryption, like 2G, making it easier to intercept data and communications.
Broad Area Coverage:
- Due to multi-band operation, a multi-frequency IMSI catcher can extend coverage across multiple network types, covering more devices within a given area.
- It also has the flexibility to adjust frequency ranges based on the environment, allowing it to capture data even in locations with mixed network deployments.
Enhanced Device Identification:
- Can capture a wider array of identifiers, including IMSI, IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity), and TMSI (Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity) across different networks.
- Provides more robust tracking and identification capabilities, as it can capture these identifiers regardless of network technology, enhancing the tracking of devices moving between different network types.
Lower Detection Risk:
- By interacting with devices on the native frequency they are using (e.g., 4G if the device is on 4G), multi-frequency IMSI catchers avoid creating the noticeable network transitions (e.g., forced downgrades) that single-frequency IMSI catchers can cause.
- This minimizes the likelihood of detection by security software, which often monitors for unusual network changes as an indicator of IMSI catcher presence.
Application Scenarios of Multi-Frequency RF IMSI Catchers
High-Security Environments and Surveillance:
- Used in intelligence and national security operations to monitor suspects across cellular networks, especially in areas where mobile phones operate on different generations of cellular technology.
- Common in high-security or surveillance-sensitive environments, such as borders, airports, and high-value events, where they help track movement and gather communication metadata.
Border Control and Cross-Border Surveillance:
- Multi-frequency IMSI catchers can monitor all devices crossing borders, even if they switch networks (e.g., from one country’s 4G network to another’s 3G network).
- Helps border agencies identify and track individuals by capturing consistent data across networks and network generations.
Urban Surveillance for Crowd Control:
- Useful in urban environments with mixed network infrastructures, such as downtown areas or public event spaces where devices operate on varying network frequencies.
- Provides law enforcement or security teams with broader surveillance coverage without requiring individuals to switch networks, keeping operations discreet.
Corporate Security and Confidentiality Protection:
- Used by corporations in highly sensitive areas to detect unauthorized devices by capturing multi-network data to identify non-compliant or unauthorized devices.
- Can monitor employees’ and visitors’ devices across frequencies, ensuring no unauthorized devices are present in restricted areas.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
The use of multi-frequency IMSI catchers raises significant privacy and ethical concerns:
- Privacy Violation Risks: Given the device’s broad reach, non-targeted individuals may be monitored unknowingly, raising serious privacy concerns.
- Legal Restrictions: Many countries regulate or prohibit IMSI catcher use outside of authorized government or law enforcement agencies due to potential misuse and the risks to citizens’ data privacy.
- Data Security: Collected data must be securely stored and handled to prevent unauthorized access, as sensitive identifiers could be compromised if not properly secured.
Detection and Countermeasures
Identifying a multi-frequency RF IMSI catcher is more challenging due to its adaptability. However, specialized detection methods are emerging:
- Advanced Mobile Apps: Apps with multi-frequency analysis capability, designed to detect more subtle network anomalies.
- SDR Monitoring: SDR tools can monitor all frequencies in an area to identify unusual signal behavior across networks.
- Network Provider Monitoring: Cellular providers increasingly use internal systems to detect suspicious signal activity on their networks, alerting them to potential IMSI catcher activity across frequencies.
Multi-frequency RF IMSI catchers represent a powerful, adaptable tool for surveillance, providing unmatched flexibility across cellular networks. However, responsible and legal use, with respect for privacy rights, remains essential in deploying such sophisticated technology.
RF IMSI Catcher in the Wild
When found “in the wild,” an RF IMSI catcher is usually operating covertly, blending into legitimate cellular networks while intercepting data from nearby mobile devices. Law enforcement and intelligence agencies frequently use these devices for tracking suspects, but they are also sometimes deployed by unauthorized groups, including private investigators and malicious actors. Here’s how RF IMSI catchers can be observed and detected when they are active in public spaces:
Typical Deployment Locations and Purposes
Urban Centers and High-Crime Areas:
- Purpose: Law enforcement often uses IMSI catchers in high-crime areas to monitor potential criminal activity. These devices can gather IMSI data from mobile phones to identify and track suspects.
- Indicators: Unusual network behavior, such as devices dropping from 4G or 5G to 2G without reason, may indicate an IMSI catcher nearby. This is particularly common when the device is mobile, such as in police vehicles equipped with IMSI catcher technology.
Public Events and Large Gatherings:
- Purpose: During large public events (concerts, rallies, protests), authorities may deploy IMSI catchers to monitor crowd activity and identify individuals associated with criminal or disruptive activities.
- Indicators: Attendees might notice fluctuating network connectivity or suspiciously high battery drain on their devices, especially in areas where cellular networks should otherwise be strong and stable.
Sensitive Locations (Airports, Borders, Government Buildings):
- Purpose: IMSI catchers are used at locations with high security concerns to detect and track individuals who may pose threats, as well as to prevent illegal communications in sensitive areas.
- Indicators: People at these locations might experience lower network quality, or in some cases, be unable to connect to their typical mobile carrier. Some mobile devices may also revert to older network types.
Industrial Espionage and Corporate Surveillance:
- Purpose: In competitive industries or corporations handling sensitive information, IMSI catchers are sometimes used (often illegally) to monitor employee communications and detect unauthorized devices within restricted areas.
- Indicators: Employees may notice unusual network behavior, such as devices failing to connect to secure 4G or 5G networks within corporate offices, or may experience intermittent connectivity that is resolved upon leaving the premises.
Private Surveillance (Unauthorized Use):
- Purpose: Some private investigators and unauthorized individuals deploy IMSI catchers to gather personal data or monitor individuals. This is an illegal use in many countries but remains a concern in certain cases.
- Indicators: People under unauthorized surveillance may notice excessive battery drain, frequent network downgrades, and unusual data activity. In some cases, devices may experience “ghost” calls, where the phone indicates a call but there is no active conversation.
Detecting an RF IMSI Catcher
Mobile Applications:
- SnoopSnitch and AIMSICD: These apps can help detect abnormal tower behavior, like fake towers or unusual network downgrades, based on device data and cell tower changes.
- Limitations: These apps work best on Android devices with specific permissions or rooted access, as iOS restrictions limit access to necessary data.
Signal Analysis with Software-Defined Radio (SDR):
- SDR Tools: Using SDR, professionals can monitor and analyze RF signals in real time, looking for anomalies in cell tower identifiers, frequencies, or protocols that could indicate an IMSI catcher.
- Challenges: SDR tools require technical knowledge and equipment to analyze and interpret signal data accurately.
Hardware Solutions and Security Systems:
- Detection Devices: Some security firms offer dedicated IMSI catcher detection devices that continuously monitor cellular traffic for unusual patterns. These are often used in sensitive locations like government buildings.
- Advantages: These devices provide real-time alerts for suspicious cellular activity, offering a reliable way to detect potential IMSI catchers.
Crowdsourced Detection Networks:
- Collaborative Alerts: Platforms that aggregate data from multiple users, such as OpenCellID and other crowdsourced databases, allow for tracking of cell towers over time, making it easier to spot temporary or suspicious towers.
Countermeasures and Best Practices
Device Settings:
- Disable 2G Networks: If possible, disable 2G on devices to prevent them from connecting to the older, less secure networks often exploited by IMSI catchers.
- Airplane Mode: Activating airplane mode in high-risk areas can prevent unsolicited connections. However, this may not always be practical if mobile connectivity is needed.
Awareness and Education:
- Educating employees or the public about IMSI catchers and their signs (network downgrades, excessive battery drain) helps individuals take steps to protect their data and report suspicious activity.
Regular Network Audits:
- For organizations, conducting regular network and signal audits in sensitive areas can help identify and mitigate IMSI catcher threats, either through in-house or third-party services.
Overall, IMSI catchers deployed in public spaces, whether for authorized or unauthorized purposes, can be detected with the right tools and vigilance, although they continue to pose significant privacy and security concerns.
RF IMSI Catcher Detection
8 Methods of Detection
- Signal Strength Analysis: Monitoring variations in signal strength can help detect the presence of an RF IMSI catcher. Unusual or stronger signals may indicate the presence of a surveillance device.
- Network Anomalies: Detecting anomalies in the network, such as unexpected changes in cell tower connections, can signal the presence of an RF IMSI catcher.
- Device Behavior Monitoring: Monitoring unusual behavior in mobile devices, such as sudden changes in network connectivity or increased data usage, can indicate interference from an RF IMSI catcher.
- Spectrum Analysis: Using spectrum analyzers to scan the RF spectrum can help identify unusual signals or frequencies associated with IMSI catchers. In addition to spectrum analysis, understanding the IMSI catcher range is crucial when identifying potential threats. While spectrum analyzers scan the RF spectrum to detect unusual signals or frequencies associated with IMSI catchers, knowing the effective range of these devices allows for more precise detection and tracking. IMSI catchers typically operate within a certain radius, and being aware of this range helps narrow down the area where suspicious activity might occur.
- Signal Pattern Recognition: Analyzing signal patterns for irregularities can reveal the presence of an RF IMSI catcher. Patterns that do not match known cell tower signals may indicate a surveillance device.
- Physical Inspection: Conducting physical inspections of environments, such as public spaces or corporate facilities, can help detect hidden RF IMSI catchers.
- RF Detection Apps: Utilizing specialized RF detection apps on mobile devices can assist in identifying the presence of IMSI catchers by monitoring for suspicious signals.
- Professional Equipment: Employing professional-grade RF detection equipment can provide accurate and reliable detection of IMSI catchers. Professional RF detection tools can identify the specific frequencies and signal patterns associated with IMSI catcher technology, making it easier to pinpoint their presence and mitigate the risks they pose to privacy and security.
8 Detection Tools
- RF Spectrum Analyzers: These devices analyze the RF spectrum to identify unusual signals and frequencies associated with IMSI catchers.
- Signal Detectors: Handheld signal detectors can help in locating sources of RF interference and identifying potential IMSI catchers.
- Network Scanners: Network scanners monitor network traffic and identify anomalies that may indicate the presence of an RF IMSI catcher.
- Mobile Detection Apps: Apps designed to detect RF signals can be used to monitor for suspicious activity and identify potential IMSI catchers.
- Directional Antennas: Directional antennas help in locating the source of RF signals by focusing on specific directions and detecting signals from known IMSI catchers.
- Interference Detectors: These tools detect and measure interference in the RF spectrum, which can help identify IMSI catchers.
- Jammers: RF jammers can disrupt the signals of IMSI catchers, although their use is regulated and may not always be legal.
- Surveillance Detection Systems: Comprehensive surveillance detection systems offer advanced features for detecting and countering IMSI catchers and other surveillance devices.

Top RF Signal Detector Features You Should Know About
Using HackRF with RF IMSI Catcher
HackRF is an open-source software-defined radio (SDR) platform designed to work with a wide range of RF signals. It offers a versatile and powerful tool for RF enthusiasts, researchers, and professionals involved in signal detection and analysis. As a low-cost, flexible hardware, HackRF is frequently utilized in various RF applications, including as a tool for RF IMSI catching.
The HackRF hardware is known for its broad frequency coverage, ranging from 1 MHz to 6 GHz, which allows it to capture a wide spectrum of signals. Its software integration capabilities and compatibility with various software packages make it an appealing choice for those needing detailed and comprehensive RF monitoring.
Integration and 8 Use Cases
Integration with RF IMSI Catchers:
HackRF can be integrated with RF IMSI catchers to enhance their capabilities. By using HackRF, users can extend the frequency range and improve the sensitivity of IMSI catching operations. The combination of HackRF with specialized IMSI catching software provides a robust platform for monitoring and analyzing mobile network traffic.
8 Use Cases:
- Signal Analysis: HackRF’s ability to cover a broad frequency range allows it to analyze different types of signals. When used with RF IMSI catchers, it helps in identifying and decoding signals from IMSI catchers operating within the same frequency spectrum.
- Spectrum Monitoring: HackRF can continuously monitor the RF spectrum for unusual or unauthorized activity, making it easier to detect the presence of IMSI catchers. This is particularly useful in high-security areas where IMSI catching may pose a threat.
- Frequency Scanning: By integrating HackRF with IMSI catching software, users can perform detailed frequency scans to locate potential IMSI catchers. This functionality is vital for identifying hidden surveillance devices.
- Signal Jamming Detection: HackRF’s wide frequency range helps in detecting jamming signals that may be used by IMSI catchers to obscure their presence or disrupt communications.
- Mobile Network Traffic Analysis: HackRF can be used to capture and analyze mobile network traffic in conjunction with IMSI catchers, providing insights into the behavior and operation of these devices.
- Testing and Calibration: HackRF is useful for testing and calibrating RF IMSI catcher, ensuring they operate within their specified frequency ranges and meet performance standards.
- Educational Purposes: HackRF, combined with IMSI catchers, serves as an educational tool for learning about RF signal detection, mobile networks, and security.
- Research and Development: In research settings, HackRF can be used to develop and test new IMSI catching techniques and technologies, contributing to advancements in RF monitoring and security.
Buying an RF IMSI Catcher
12 Factors to Consider
When purchasing an RF IMSI catcher, several key factors should be taken into account to ensure that the device meets your needs and provides effective performance:
- Frequency Range: Ensure that the RF IMSI catcher covers the frequency ranges relevant to your needs. A wider frequency range allows for more comprehensive monitoring of various communication signals.
- Detection Sensitivity: The sensitivity of the device affects its ability to detect weak signals. A higher sensitivity ensures that even low-power IMSI catchers can be detected.
- Accuracy: Consider the accuracy of the IMSI catcher in identifying and distinguishing between different types of signals. High accuracy is crucial for reliable detection.
- Portability: Depending on your usage scenario, the size and weight of the device may be important. Portable devices are useful for fieldwork and on-the-go detection.
- Ease of Use: Look for an IMSI catcher that is user-friendly, with an intuitive interface and clear instructions. This will make operation and setup more straightforward.
- Integration Capabilities: Check if the device can be integrated with other tools and software, such as HackRF, for enhanced functionality and analysis.
- Power Source: Consider the power requirements and battery life of the IMSI catcher. Devices with longer battery life or flexible power options may be more practical for extended use.
- Cost: Evaluate the cost of the device relative to its features and performance. While higher-priced models may offer advanced capabilities, ensure that the investment aligns with your needs.
- Brand Reputation: Research the reputation of the manufacturer and the reliability of their products. Reviews and user feedback can provide insights into the quality and performance of the device.
- Warranty and Support: Look for products that come with a warranty and reliable customer support. This can be crucial in case of any issues or malfunctions with the device.
- Legal Considerations: Ensure that the IMSI catcher complies with local regulations and legal requirements. Unauthorized use of IMSI catchers can have legal consequences.
- Software Compatibility: Check the compatibility of the IMSI catcher with available software tools for signal analysis and monitoring. This can enhance the device’s functionality and usability.
Where to Buy
When looking to purchase an RF IMSI catcher, consider exploring reputable sources such as specialized electronic equipment suppliers, security technology providers, and dedicated RF equipment stores. Ensure that the sellers have a good reputation and offer reliable products. Avoid unauthorized or unverified sources to reduce the risk of acquiring substandard or illegal equipment.
RF IMSI Catcher: Risks and Ethical Concerns
8 Privacy Issues
The use of RF IMSI catcher raises several privacy concerns, particularly regarding unauthorized surveillance and data collection:
- Unauthorized Surveillance: IMSI catchers can intercept mobile communications without the knowledge or consent of the individuals being monitored, leading to privacy violations.
- Data Security: The intercepted data can include sensitive personal information, which poses risks if it falls into the wrong hands or is misused.
- Targeted Tracking: IMSI catchers can be used to track individuals’ movements and behaviors, raising concerns about unauthorized tracking and monitoring.
- Data Misuse: There is a risk that intercepted data could be used for malicious purposes or unauthorized sharing, compromising personal and organizational security.
- Lack of Transparency: The deployment of IMSI catchers often lacks transparency, making it difficult for individuals to know if they are being monitored.
- Legal Implications: The use of IMSI catchers without proper authorization can lead to legal repercussions, including violations of privacy laws and regulations.
- Ethical Concerns: The ethical implications of using IMSI catchers involve balancing security needs with respect for individual privacy and civil liberties.
- Public Trust: Unauthorized surveillance can erode public trust in security and law enforcement agencies, affecting their credibility and effectiveness.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The deployment and use of RF IMSI catchers must be approached with careful consideration of legal and ethical standards:
- Legal Compliance: Ensure that the use of IMSI catchers complies with local, national, and international laws regarding surveillance and privacy.
- Authorization Requirements: Obtain necessary authorizations and approvals before deploying IMSI catchers, especially for law enforcement and security purposes.
- Ethical Use: Use IMSI catchers responsibly, focusing on legitimate security and investigative purposes while respecting individuals’ privacy rights.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Adhere to regulatory frameworks that govern the use of surveillance technology, including data protection and privacy regulations.
- Transparency: Maintain transparency in the deployment of IMSI catchers, informing affected parties when required and providing clear justification for their use.
- Data Handling: Implement strict protocols for handling and storing intercepted data to prevent unauthorized access and misuse.
- Accountability: Ensure that those using IMSI catchers are accountable for their actions and that there are mechanisms in place to address potential abuses.
- Public Engagement: Engage with the public and relevant stakeholders to discuss the implications of IMSI catchers and address any concerns or objections.
Applications and Use Cases for RF Scanner Signal Detector
Future Trends in RF IMSI Catcher
The field of RF IMSI catcher is rapidly evolving as technological advancements continue to shape the landscape of mobile communication and surveillance. Understanding these future trends is crucial for staying informed about the capabilities and implications of RF IMSI catchers. This section explores anticipated technological advancements and their potential impacts on privacy and security.
Technological Advances
1. Enhanced Detection Capabilities:
The future of RF IMSI catchers is likely to see significant improvements in detection capabilities. Emerging technologies, such as advanced signal processing algorithms and machine learning, will enable RF IMSI catchers to more accurately identify and differentiate between various types of RF signals. This will reduce false positives and improve the efficiency of IMSI catchers in detecting and intercepting targeted signals.
2. Miniaturization and Portability:
Technological advancements will drive the miniaturization of RF IMSI catchers. As components become smaller and more efficient, the physical size of these devices will decrease while maintaining or enhancing their performance. Portable RF IMSI catchers will become more compact and lightweight, making them easier to use in various environments without compromising on their detection capabilities.
3. Integration with Other Surveillance Tools:
RF IMSI catchers will increasingly be integrated with other surveillance technologies, such as mobile signal jammers, GPS tracking systems and high-resolution cameras. This integration will provide a more comprehensive monitoring solution, allowing for simultaneous tracking of mobile signals and visual data. Such advancements will enhance the effectiveness of surveillance operations and improve the overall accuracy of data collection.
4. Improved Signal Processing and Filtering:
Future RF IMSI catchers will benefit from advancements in signal processing and filtering technologies. Enhanced signal processing will enable these devices to handle complex signal environments and filter out irrelevant or noise signals more effectively. This will lead to more precise detection of IMSI signals and a reduction in interference from non-target signals.
5. Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Artificial Intelligence (AI) will play a significant role in the future development of RF IMSI catchers. AI algorithms will be employed to analyze and interpret large volumes of RF data, enabling more sophisticated pattern recognition and anomaly detection. AI-powered RF IMSI catchers will be able to identify and classify signals with greater accuracy, providing more actionable intelligence.
6. Advanced Encryption and Security Measures:
As RF IMSI catchers become more advanced, so too will the encryption and security measures implemented within these devices. Future developments will focus on enhancing the security of RF IMSI catchers to prevent unauthorized access and ensure that the data collected is protected from tampering or interception. This will be crucial for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of surveillance operations.
7. Wider Frequency Range:
The frequency range covered by RF IMSI catchers is expected to expand significantly. Future models will be capable of detecting a broader spectrum of frequencies, including those used by emerging communication technologies. This expanded range will ensure that RF IMSI catchers remain effective in monitoring new and evolving communication protocols.
8. Enhanced User Interfaces:
User interfaces for RF IMSI catchers will become more intuitive and user-friendly. Advances in software design and touch screen technology will provide operators with more accessible and informative interfaces. Improved user interfaces will streamline the operation of RF IMSI catchers and facilitate easier configuration and monitoring.
Impact on Privacy and Security
1. Increased Surveillance Capabilities:
As RF IMSI catchers become more advanced, their surveillance capabilities will expand. This increased capability will enable more comprehensive monitoring of mobile communications, raising concerns about privacy invasion. The ability to track and intercept signals with greater precision could lead to more widespread and intrusive surveillance practices.
2. Potential for Abuse:
The enhanced functionality of RF IMSI catchers could lead to their misuse by unauthorized individuals or entities. The advanced features and capabilities of future RF IMSI catchers might attract malicious actors who could use these devices for illegal activities, such as unauthorized monitoring of individuals or organizations. Ensuring proper regulation and oversight will be essential to prevent misuse.
3. Privacy Regulations and Compliance:
With the evolution of RF IMSI catchers, there will likely be increased emphasis on privacy regulations and compliance. Governments and regulatory bodies will need to establish and enforce guidelines to ensure that the use of RF IMSI catchers aligns with privacy laws and protects individuals’ rights. Stricter regulations will be required to address the potential impact on personal privacy.
4. Ethical Considerations:
The advancements in RF IMSI catcher technology will prompt ethical discussions about the balance between security and privacy. As surveillance capabilities become more sophisticated, it will be important to consider the ethical implications of using RF IMSI catchers. Ensuring transparency and accountability in the use of these devices will be critical to addressing ethical concerns.
5. Public Awareness and Education:
Increased awareness and education about RF IMSI catchers will be necessary as technology advances. Educating the public about the capabilities and limitations of these devices will help individuals understand their rights and the potential impact on their privacy. Public awareness campaigns and educational programs will play a key role in promoting informed discussions about RF IMSI catchers.
6. Technological Countermeasures:
As RF IMSI catchers evolve, so will the development of countermeasures designed to protect against their detection and interception. Researchers and technology developers will focus on creating advanced countermeasures to safeguard communications and prevent unauthorized monitoring. This ongoing technological arms race will drive innovation in both RF IMSI catching and counter-surveillance technologies.
7. Impact on Communication Security:
The advancements in RF IMSI catching technology will have implications for overall communication security. The ability to intercept and analyze mobile communications with greater accuracy may prompt the development of new encryption and security measures to protect sensitive information. Ensuring robust security protocols will be essential to mitigating risks associated with advanced RF IMSI catchers.
8. Legal and Policy Implications:
The future of RF IMSI catchers will necessitate updates to legal and policy frameworks governing their use. Policymakers will need to address the challenges posed by advanced surveillance technologies and establish clear guidelines for their deployment. Ensuring that legal frameworks keep pace with technological advancements will be crucial for maintaining a balance between security and privacy.
The future trends in RF IMSI catchers reflect ongoing advancements in technology that will enhance their capabilities and impact. While these developments offer exciting possibilities for improving surveillance and monitoring, they also raise important considerations for privacy, security, and ethics. Staying informed about these trends will be essential for navigating the evolving landscape of RF IMSI catching.
FAQs about RF IMSI Catcher
The legality of IMSI catchers varies significantly depending on the country and its specific laws and regulations. Generally, IMSI catchers are legal for use by law enforcement and government agencies under strict regulations and judicial oversight. These devices are used to intercept and monitor mobile phone signals and are typically employed in criminal investigations or national security operations. However, unauthorized use of IMSI catchers is illegal and considered a serious breach of privacy laws. Individuals or entities using IMSI catchers without proper authorization can face severe legal consequences, including fines and imprisonment. Always ensure that any use of such devices complies with local laws and regulations to avoid legal issues.
IMSI catchers, traditionally designed to intercept signals from older generations of mobile networks like 2G, 3G, and 4G, are increasingly being adapted to work with 5G networks. The fundamental technology behind IMSI catchers involves capturing and analyzing mobile phone signals, which can be adjusted to interact with the different frequencies and protocols used by 5G networks. However, the effectiveness of IMSI catchers on 5G can vary due to the advanced encryption and security features introduced in 5G technology. The transition to 5G has prompted updates in interception technologies to keep pace with evolving network standards, but challenges remain in fully adapting IMSI catchers to new network architectures.
The range of an IMSI catcher can vary based on several factors, including the device’s power, the environment, and the network’s signal strength. Generally, IMSI catchers can detect and intercept signals within a radius of a few hundred meters to several kilometers. In urban areas with dense cell networks, the effective range might be shorter due to signal interference and network congestion. In contrast, in more open or rural areas with less signal traffic, the range can be extended. The actual performance and range depend on the specific model and configuration of the IMSI catcher, as well as the local regulatory constraints on transmission power.
An IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) number is a unique identifier associated with a mobile subscriber and is used primarily for network management and authentication purposes. With access to an IMSI number, one can potentially track the location of the mobile device associated with that number, intercept calls and messages, and access other types of mobile communication data. In legitimate scenarios, IMSI numbers help network operators manage connections and ensure secure communications. However, unauthorized access to IMSI numbers and the use of this information for tracking or intercepting communications without consent is illegal and constitutes a severe invasion of privacy. It is crucial to use IMSI numbers within the bounds of the law and for ethical purposes.

































