RF signal detectors play a crucial role in modern technology by identifying and analyzing radio frequency signals. intelligent RF signal detector specifically designed to detect and identify radio frequency waves, or RF waves that many devices. These devices are essential for various applications, including communication, security, and electronics. The concept of an “intelligent” RF signal detector introduces advanced features that enhance traditional capabilities. Unlike standard detectors, intelligent RF signal detectors incorporate sophisticated algorithms and data analysis to provide more precise and reliable results. This integration of intelligence improves the accuracy and functionality of RF detection, allowing for better signal identification and reduced interference. As technology evolves, intelligent RF signal detectors are becoming increasingly vital for applications requiring enhanced performance and efficiency.
What are Intelligent RF Signal Detectors
Definition and Functionality
An intelligent RF signal detector is designed to go beyond basic RF signal detection. What sets these devices apart is their advanced signal processing capabilities and smart detection algorithms. Traditional RF signal detectors might only provide basic signal strength readings, but an intelligent RF signal detector incorporates a range of sophisticated technologies. These include digital signal processing (DSP), machine learning algorithms, and real-time data analysis. Such features enable the device to not only detect signals but also to analyze their patterns, identify potential sources of interference, and filter out noise. The result is a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the RF environment.
Benefits of Intelligence in RF Detection
The integration of intelligence into RF signal detectors auto provides numerous advantages over traditional models. Below is a comparison table highlighting the key benefits:
| Feature | Traditional RF Signal Detectors | Intelligent RF Signal Detectors |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Processing | Basic, often analog processing | Advanced, digital processing |
| Detection Algorithms | Simple, less adaptive | Smart, adaptive, and learning |
| Accuracy | Lower, prone to interference | Higher, with better noise filtering |
| Real-Time Analysis | Limited or non-existent | Extensive and immediate |
| Signal Identification | Basic signal strength readings | Detailed pattern analysis |
| User Customization | Minimal | Extensive, with adjustable settings |
By incorporating these intelligent features, the intelligent RF signal detector not only improves detection accuracy but also enhances the ability to interpret and respond to complex RF environments effectively. This makes it a valuable tool for applications that demand high precision and reliability.
How to use rf signal detector:
Power On: Turn on the RF detector by pressing the power button or switching it on.
Select Frequency Range (if available): Choose the frequency band or sensitivity level to match the type of signal you are detecting (e.g., wireless cameras, GPS trackers, audio bugs).
Scan the Area: Move the detector slowly around the area you want to check. Pay special attention to objects where bugs may be hidden, such as electronics, light fixtures, or furniture.
Monitor the Signal Strength: Watch the signal strength meter or listen for audible beeps. A rising signal level or faster beeping indicates you are getting closer to the source.
Pinpoint the Source: Adjust sensitivity if needed—reduce it to narrow down the exact location when close to a signal. Some detectors may also allow you to switch between vibration or sound modes to make pinpointing easier.
Check for False Alarms: Turn off nearby Wi-Fi devices or known RF sources to avoid interference or false readings.
Repeat if Necessary: Rescan the area to ensure no other suspicious signals are present.
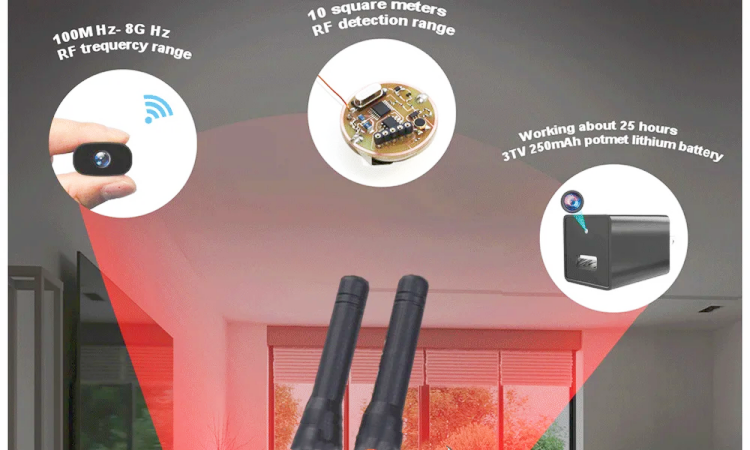

Intelligent RF Signal Detector Specifications
- Frequency Range:
- The detector should cover a wide frequency range, typically from 1 MHz to 6 GHz, enabling it to identify various RF signals, including those from Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks.
- Sensitivity:
- High sensitivity levels, often around -120 dBm, allowing the detector to pick up weak signals effectively.
- Dynamic Range:
- A dynamic range of at least 80 dB ensures that the device can differentiate between strong and weak signals without distortion.
- Detection Modes:
- Multiple detection modes, including continuous scanning, peak hold, and signal averaging, to provide versatility in monitoring environments.
- Signal Identification:
- The ability to classify and identify different types of signals (e.g., analog, digital, pulsed) for comprehensive analysis.
- Display:
- A user-friendly interface with an LCD or OLED display to show signal strength, frequency, and type of detected signals in real-time.
- Data Logging:
- Built-in memory or SD card support for data logging, allowing users to store and analyze signal data over time.
- Connectivity:
- Options for USB, Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi connectivity for easy data transfer to computers or mobile devices.
- Battery Life:
- Long battery life (e.g., 10 hours or more) with options for rechargeable batteries and power-saving modes.
- Portability:
- Compact and lightweight design for easy transport and use in various locations, making it suitable for fieldwork.
- Calibration:
- Automatic calibration features to maintain accuracy over time, with the option for manual calibration by the user.
- Environmental Resistance:
- Robust construction with water and dust resistance (e.g., IP54 rating) for durability in different environments.
- Software Compatibility:
- Compatible software for advanced analysis and visualization of detected signals, allowing for detailed reporting.
- Compliance:
- Adherence to relevant regulations and standards (e.g., FCC, CE) to ensure legal operation and safety.
- User Interface:
- Intuitive menu navigation with customizable settings for experienced users and beginners alike.
These specifications ensure that an Intelligent RF Signal Detector is versatile, reliable, and effective for various applications, from personal use to professional RF analysis.
Essential Guide to Broadband RF Detector: Features and Uses
RF Detector Price of Intelligent RF Signal Detector
Cost Range
The price of an intelligent RF signal detector can vary significantly depending on its features, performance, and brand. Generally, these detectors fall into a range of approximately $200 to $2000. The lower end of the spectrum typically includes basic models with essential features and limited functionalities. In contrast, high-end models with advanced capabilities such as enhanced signal processing, smart detection algorithms, and real-time data analysis can be priced at the upper end. Factors influencing the cost include the detector’s accuracy, range, additional features like data logging or connectivity options, and the complexity of the intelligent algorithms integrated into the device.
Value for Money
When evaluating the value for money of an intelligent RF signal detector, it is crucial to consider how the features and performance justify the price. Below is a table comparing different models based on their price and key features:
| Model | Price Range | Key Features | Performance Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Model | $200 - $500 | Basic signal detection, minimal features | Good for simple applications, lower accuracy |
| Mid-Range Model | $500 - $1000 | Enhanced signal processing, moderate features | Better accuracy, suitable for varied environments |
| High-End Model | $1000 - $2000 | Advanced algorithms, real-time analysis, extensive features | High accuracy, versatile, ideal for complex scenarios |
While higher-priced intelligent RF signal detectors offer advanced features and improved performance, the choice depends on the specific needs and application requirements. For those needing precise and sophisticated RF detection, investing in a high-end model may be worthwhile. Conversely, for simpler applications, a more basic model may offer sufficient functionality at a lower cost.
How Portable RF Detector Works: Technology Behind Detection
Wireless Intelligent RF Signal Detector
The Wireless Intelligent RF Signal Detector is an advanced tool engineered for comprehensive detection and analysis of radio frequency signals. Its wireless capabilities enable remote operation, making it ideal for a variety of applications from security to telecommunications.
Functional Features
- Wide Frequency Coverage:
- The detector operates across a frequency range from 30 MHz to 6 GHz, enabling monitoring of various wireless signals, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks.
- Intelligent Signal Analysis:
- Equipped with advanced algorithms, it can analyze and identify signal types in real-time, allowing users to quickly understand the source and characteristics of detected signals.
- Wireless Connectivity:
- Supports Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connections, enabling remote monitoring and data management through smartphones or computers.
User Experience
- Intuitive Interface:
- Features a touch screen with a user-friendly interface, making signal monitoring and data analysis straightforward and accessible for users of varying expertise.
- Portability:
- Its compact and lightweight design makes it easy to carry, suitable for use in diverse environments, whether in a lab or outdoors.
- Long Battery Life:
- Optimized for over 15 hours of continuous use, ensuring that users can operate it for extended periods without frequent recharging.
Market Applications
- Security Monitoring:
- Used to detect unauthorized RF activity in sensitive areas, helping to identify potential security threats.
- Wireless Network Optimization:
- Assists businesses in evaluating and optimizing wireless network performance, ensuring signal quality and coverage.
- Scientific Research:
- Provides a valuable tool for academics collecting data on RF environments, supporting research in wireless communications and signal propagation.
Technical Advantages
- High Sensitivity and Dynamic Range:
- With a sensitivity down to -130 dBm and a dynamic range of 90 dB, the detector accurately captures signals even in complex environments.
- Automatic Calibration:
- Features built-in self-calibration to maintain accuracy and reliability over prolonged usage.
- Data Logging and Analysis:
- Supports internal storage and cloud backup for long-term data analysis and reporting capabilities.
By examining these different aspects, it becomes clear that the Wireless Intelligent RF Signal Detector offers significant value in terms of technology, user experience, and market applications, providing users with robust capabilities for signal monitoring and analysis.
How to Use Intelligent RF Signal Detector
Using an Intelligent RF Signal Detector effectively involves several steps, from initial setup to monitoring and analysis. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to use it:
1. Initial Setup
- Unboxing:
- Carefully remove the detector from its packaging and ensure all components (cables, chargers, manuals) are included.
- Charging:
- If the device is battery-operated, fully charge it before first use. Connect it to a power source using the provided charger.
- Installing Software (if applicable):
- If the detector requires software for advanced features, install it on your computer or mobile device according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2. Powering On
- Turning On the Device:
- Locate the power button and press it to turn on the device. Wait for it to boot up and initialize.
- Calibration:
- Perform any necessary calibration as per the user manual. This may involve setting baseline readings or adjusting settings based on environmental conditions.
3. Selecting Frequency Range
- Choosing Frequency:
- Use the interface to select the desired frequency range for detection (e.g., 30 MHz to 6 GHz). This may depend on the specific signals you are interested in monitoring.
4. Monitoring Signals
- Scanning Mode:
- Activate the scanning mode. The detector will start searching for RF signals within the selected frequency range.
- Signal Visualization:
- Monitor the display for real-time visualizations of detected signals. Look for indicators showing signal strength, type, and frequency.
5. Analyzing Data
- Signal Identification:
- Use the signal analysis features to identify the types of signals detected. This may include classification of signals as digital, analog, pulsed, etc.
- Data Logging:
- If your device supports data logging, enable this feature to record signal information over time for later analysis.
6. Remote Monitoring (if applicable)
- Connecting to a Mobile Device:
- If the detector has wireless capabilities, connect it to your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. This allows for remote monitoring and alerts.
- Using Companion App:
- Utilize any companion app for additional features, such as detailed analytics, historical data access, and customizable alerts.
7. Performing Advanced Functions
- Setting Alerts:
- Configure custom alerts for specific signal thresholds or types, so you are notified when significant activity is detected.
- Exporting Data:
- Export data to your computer or cloud service for further analysis or reporting. Follow the device’s guidelines for data transfer.
8. Powering Down
- Turning Off:
- After use, power down the device to conserve battery life. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for safely shutting it down.
- Storage:
- Store the detector in a safe place, ensuring it is protected from extreme temperatures and moisture.
Tips for Effective Use
- Familiarize Yourself with the Manual:
- Always refer to the user manual for specific instructions related to your model.
- Regular Calibration:
- Regularly calibrate the device to maintain accuracy, especially if you use it in varying environments.
- Stay Updated:
- Check for software updates that may enhance the functionality of the detector.
By following these steps, you can effectively utilize an Intelligent RF Signal Detector for a range of applications, ensuring you maximize its capabilities for monitoring and analyzing RF signals.

Intelligent RF Signal Detector & Bug Detectors: Professional Countersurveillance
Purpose and Functionality
- Intelligent RF Signal Detectors:
- Designed to identify, analyze, and monitor a wide range of radio frequency signals across various frequencies (e.g., 30 MHz to 6 GHz).
- Used to detect wireless communications, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular signals.
- Capable of signal classification and strength analysis, allowing users to understand the RF environment in detail.
- Bug Detectors:
- Specifically designed to locate and identify hidden surveillance devices (bugs), including audio and video transmitters.
- Focus on detecting specific frequencies used by common surveillance devices, often within a narrower frequency range.
- May include features like signal strength indicators, audio feedback, and visual alerts for easier identification of bugs.
Technical Specifications
- Frequency Range:
- RF Signal Detectors: Typically cover a broader spectrum (1 MHz to 6 GHz) for comprehensive monitoring.
- Bug Detectors: Often target specific frequencies associated with spy devices, usually around 100 MHz to 3 GHz.
- Sensitivity:
- Both devices offer high sensitivity; however, RF detectors generally have superior capabilities to detect weak signals due to their advanced technology.
- Detection Modes:
- RF Signal Detectors: Multiple modes including continuous scanning, historical analysis, and real-time monitoring.
- Bug Detectors: Usually focused on scanning for active signals, with features tailored for quick bug identification.
User Interface and Experience
- RF Signal Detectors:
- Feature advanced displays (often LCD or OLED) for real-time data visualization, signal strength graphs, and signal type identification.
- May include software compatibility for detailed analysis and reporting.
- Bug Detectors:
- Typically have simpler interfaces with signal strength indicators and audible alerts, making them user-friendly for rapid assessments.
Counter Surveillance Techniques
- Intelligent RF Signal Detectors:
- Provide detailed insights into all RF activity, allowing users to identify unauthorized signals or interference that could indicate surveillance.
- Enable users to assess the RF environment, helping to enhance overall security strategies.
- Bug Detectors:
- Offer a more focused approach to countersurveillance by actively seeking out and locating potential surveillance devices.
- Often used in conjunction with RF detectors for comprehensive surveillance detection.
While both Intelligent RF Signal Detectors and Bug Detectors play critical roles in professional countersurveillance, they serve different purposes and applications. Intelligent RF Signal Detectors offer a broader range of capabilities for monitoring various RF signals, making them ideal for detailed analysis. In contrast, Bug Detectors are specialized tools designed for quickly identifying hidden surveillance devices. Together, they provide a robust solution for ensuring privacy and security against unauthorized monitoring.
RF Detector App About Intelligent RF Signal Detector
Overview of RF Detector Apps
RF detector apps are mobile applications designed to assist users in detecting and analyzing radio frequency signals using their smartphones or tablets. These apps leverage the device’s built-in sensors and processing power to provide RF detection capabilities. While they offer convenience and portability, their performance can vary depending on the app’s design and the hardware capabilities of the mobile device. Some apps are designed to complement physical RF detectors, including intelligent RF signal detectors, while others aim to serve as standalone solutions for basic RF signal detection.
Features and Limitations
When comparing RF detector apps to physical intelligent RF signal detectors, there are several features and limitations to consider. Here’s a detailed look at each:
Features of RF Detector Apps
- Convenience and Portability: RF detector apps are easily accessible on smartphones, allowing users to detect signals on-the-go without needing additional equipment.
- Cost-Effective: Many RF detector apps are available for free or at a low cost, making them a budget-friendly option for casual users.
- Basic Signal Detection: Apps can provide basic functionality such as signal strength indicators and simple frequency analysis.
- Real-Time Updates: Some apps offer real-time signal monitoring and alerts, which can be useful for quick checks.
Limitations of RF Detector Apps
- Limited Accuracy: Compared to physical intelligent RF signal detectors, apps may lack precision and sensitivity due to the constraints of smartphone sensors.
- Hardware Dependency: The performance of RF detector apps depends heavily on the quality of the smartphone’s hardware, which may not be optimized for RF detection.
- Limited Range: Apps generally have a shorter detection range and may not be able to detect weaker signals or those from greater distances.
- Less Advanced Features: Apps often lack advanced features such as detailed signal analysis, sophisticated filtering, and extensive data logging found in intelligent RF signal detectors.
While RF detector apps offer a convenient and cost-effective solution for basic signal detection, they generally fall short in accuracy and functionality compared to dedicated intelligent RF signal detectors. For more advanced and precise needs, investing in a physical RF detector might be necessary.
Unveiling the Most Accurate RF Signal Detector Models
Intelligent RF Signal Detector Online
Purchasing Options
When looking to buy an intelligent RF signal detector online, several trusted retailers and platforms offer a range of options. Here are some recommended sources:
- Specialized Electronics Retailers: Websites such as SZMID provides a variety of RF detection equipment, including advanced models like the intelligent RF signal detector. These retailers are known for their technical expertise and quality assurance.
- Manufacturer Websites: Purchasing directly from the manufacturer’s website, such as SZMID, can provide access to the latest models and detailed product information about intelligent RF signal detectors. This option often includes direct support and warranty services.
Online Reviews and Ratings
Customer reviews and ratings can be crucial in deciding which intelligent RF signal detector to purchase. Here’s an overview of what to look for:
- SZMID Reviews: SZMID features extensive customer feedback on various RF detectors. Look for models with high ratings and detailed reviews, which can provide insights into the detector’s performance and reliability.
- Manufacturer Reviews: Direct feedback from manufacturers’ websites or forums related to the product can offer specialized insights into the performance and features of intelligent RF signal detectors.
- Tech Review Sites: Websites such as SZMIDoften conduct in-depth reviews of electronics, including RF detectors. These reviews can provide professional evaluations of the detector’s functionality, comparing different models and highlighting pros and cons.
Purchasing an intelligent RF signal detector online involves exploring trusted retailers and platforms, while considering customer reviews and ratings to ensure informed decision-making. Each option provides a different perspective on the product’s quality and performance, helping you choose the best detector for your needs.
Intelligent RF Signal Detector Device
Types of Devices
RF signal detectors come in various forms to suit different needs and applications. Here’s an overview of the main types of devices, including those that incorporate intelligent RF signal detectors:
- Handheld Models: These are portable and user-friendly, designed for on-the-go detection. Handheld intelligent RF signal detectors are ideal for fieldwork or quick signal checks. They typically offer a balance between functionality and convenience, allowing users to easily scan for RF signals in different environments.
- Desktop Units: Desktop RF detectors are generally more powerful and offer advanced features compared to handheld models. These units are designed for stationary use and are equipped with more sophisticated signal processing capabilities. Intelligent RF signal detectors in this category often include extensive data analysis tools and higher sensitivity.
- Integrated Systems: These are comprehensive setups that combine RF detection with other systems for enhanced functionality. For example, some intelligent RF signal detectors are integrated into security systems or communication networks, providing real-time monitoring and advanced detection features.
- Vehicle-Mounted Devices: Designed for use in vehicles, these RF detectors offer constant monitoring of the RF environment while on the move. They are useful for applications such as counter-surveillance or communication monitoring in transit, and often include intelligent RF signal detection features for enhanced performance.
Features to Consider
When selecting an intelligent RF signal detector, several key features should be considered to ensure the device meets your needs:
- Frequency Range: The frequency range determines the spectrum of signals the detector can detect. An intelligent RF signal detector with a broad frequency range can identify a wider array of signals, making it versatile for various applications.
- Sensitivity: Sensitivity affects the detector’s ability to pick up weak signals. High sensitivity in an intelligent RF signal detector allows for the detection of low-level signals, which is crucial for accurate signal analysis and detection.
- Detection Modes: Different modes such as pulse detection, continuous wave detection, or frequency hopping can enhance the functionality of an RF detector. Intelligent RF signal detectors often feature multiple detection modes to handle different types of RF signals and interference.
- Data Analysis and Display: Advanced models include features for real-time data analysis and visualization. Look for detectors with digital displays, data logging capabilities, and graphical representations of signal strength and patterns, which are typical of intelligent RF signal detectors.
RF detectors come in various forms, each suited for specific uses, from handheld and desktop models to integrated systems and vehicle-mounted devices. When choosing an intelligent RF signal detector, consider features such as frequency range, sensitivity, detection modes, and data analysis capabilities to ensure you select a device that meets your detection and analysis needs.
Intelligent RF Bug Signal Detector
Purpose and Application
Best RF bug detectors are specialized devices used to identify hidden bugs and surveillance devices that operate using radio frequency signals. These detectors are crucial for ensuring privacy and security in various settings, including personal spaces, corporate environments, and sensitive meetings. Intelligent RF signal detectors are particularly effective in this context due to their advanced features and enhanced detection capabilities.
- Personal Security: Individuals concerned about personal privacy can use RF bug detectors to scan their homes or personal spaces for unauthorized surveillance devices.
- Corporate Espionage Prevention: Businesses utilize RF bug detectors to safeguard confidential meetings and proprietary information from being intercepted by hidden listening devices.
- Government and Law Enforcement: Agencies employ RF bug detectors to ensure that secure facilities are not compromised by clandestine surveillance equipment.
- Event and Conference Security: Event organizers use RF bug detectors to protect sensitive discussions and information from being secretly recorded or monitored.
How They Work
Intelligent RF signal detectors used as RF bug detectors rely on several technologies to effectively locate hidden bugs and surveillance devices. Here’s a detailed look at how these devices function:
- Signal Detection: RF bug detectors identify and measure radio frequency signals emitted by surveillance devices. Intelligent RF signal detectors use advanced algorithms to distinguish between legitimate signals and potential threats.
- Frequency Scanning: These detectors scan a broad range of frequencies to detect any anomalies or unusual signals that might indicate the presence of hidden bugs. Intelligent models offer extended frequency ranges and improved scanning capabilities.
- Signal Analysis: Once a potential signal is detected, the detector analyzes the signal’s characteristics to determine its source. Intelligent RF signal detectors employ sophisticated signal processing techniques to enhance detection accuracy and reduce false positives.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Many RF bug detectors provide real-time monitoring and alerts when suspicious signals are detected. Intelligent RF signal detectors often feature real-time data visualization, allowing users to see the strength and location of detected signals instantly.
RF bug detectors are essential tools for identifying hidden surveillance devices and ensuring privacy and security. By leveraging the advanced capabilities of intelligent RF signal detectors, users can effectively locate and analyze RF signals to detect and mitigate unauthorized surveillance activities.
Intelligent RF Signal Detectorfor Hidden Cameras
Detection Methods
The Hidden Camera Detector Laser, combined with RF signal detectors are essential tools for locating hidden cameras that operate using radio frequency signals. Intelligent RF signal detectors offer advanced features and methods for effectively finding these covert surveillance devices. Here’s a detailed look at how these detectors work to identify hidden cameras:
- Frequency Scanning: Hidden cameras transmit signals on various frequencies. RF detectors scan a wide range of frequencies to detect any emissions from these devices. Intelligent RF signal detectors use advanced scanning algorithms to cover more frequencies and increase the likelihood of detecting hidden cameras.
- Signal Strength Analysis: Once a signal is detected, the detector measures its strength. Hidden cameras often emit low-level signals, so an intelligent RF signal detector’s high sensitivity is crucial for picking up weak signals and locating the camera’s source.
- Signal Identification: Intelligent RF signal detectors analyze the characteristics of detected signals to distinguish between different types of RF emissions. This analysis helps in identifying whether a signal comes from a hidden camera or another electronic device.
- Directional Detection: Some RF detectors feature directional antennas that help pinpoint the exact location of the signal source. This feature is particularly useful for narrowing down the search area and accurately locating hidden cameras.
Best Practices
To effectively use an RF detector for locating hidden cameras, follow these best practices:
- Systematic Scanning: Conduct a thorough and systematic scan of the area, including common hiding spots such as smoke detectors, electrical outlets, and ventilation systems. An intelligent RF signal detector’s broad scanning capabilities will help cover all potential areas where hidden cameras might be placed.
- Check Signal Strength: Pay close attention to the strength of detected signals. Weak signals may indicate a hidden camera’s presence. Intelligent RF signal detectors with high sensitivity can help identify these faint signals more effectively.
- Analyze Detected Signals: Use the signal analysis features of your intelligent RF signal detector to assess the nature of detected signals. Understanding the signal patterns and frequencies can help determine if the source is a hidden camera or another type of RF device.
- Use Directional Features: When using an RF Signal Detector, a key factor in its effectiveness is RF signal detector rating and the presence of directional features. Higher-rated detectors often come equipped with directional antennas or signal strength indicators, which help users locate hidden cameras more precisely. To maximize efficiency, move the detector around while using these features to determine the exact direction and proximity of the hidden camera, ensuring a more accurate detection.
Intelligent RF signal detectors are powerful tools for finding hidden cameras by scanning frequencies, analyzing signal strength, and utilizing directional detection features. By following best practices such as systematic scanning and signal analysis, users can effectively locate and identify covert surveillance equipment.
FAQs About Intelligent RF Signal Detector
An RF (Radio Frequency) signal detector is a device designed to detect and measure radio frequency signals in a given area. These detectors are used for various purposes, including identifying the presence of hidden electronic devices, monitoring signal strength, and analyzing communication frequencies. RF signal detectors are essential tools in security, counter-surveillance, and electronic troubleshooting. They work by scanning a range of frequencies and detecting any RF emissions from sources such as wireless cameras, hidden microphones, or communication devices. The technology used in RF signal detectors varies, with advanced models featuring intelligent signal processing capabilities to enhance detection accuracy and reduce interference. By providing real-time data on signal strength and frequency, RF signal detectors help users locate and assess RF signals effectively.
Yes, RF detectors are effective tools for detecting radio frequency signals, but their performance depends on several factors, including the quality of the device and the type of signals being detected. High-quality RF detectors, especially intelligent RF signal detectors, are designed with advanced features that enhance their ability to detect and analyze RF signals accurately. These detectors can identify a wide range of frequencies and signal types, making them useful for various applications such as locating hidden surveillance devices, monitoring communication signals, and troubleshooting electronic equipment. However, the effectiveness of an RF detector can be influenced by factors like signal strength, frequency range, and environmental conditions. It’s important to choose a detector that suits your specific needs and to understand its limitations to ensure optimal performance.
Using an RF detector involves several key steps to ensure effective detection and analysis of RF signals. First, power on the device and adjust the settings according to your needs, such as selecting the appropriate frequency range. Next, conduct a thorough scan of the area by slowly moving the detector around to cover all potential sources of RF emissions. Pay attention to any changes in the signal strength or detection indicators on the device. When a signal is detected, use the RF detector’s features to analyze its characteristics, such as frequency and strength. For more accurate results, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration and use. Regular maintenance and understanding the device’s capabilities will help you achieve the best performance and effectively identify RF signals in various scenarios.
RF power detectors come in various types, each designed for specific applications and measurement needs. The primary types include:
Peak Power Detectors: These detectors measure the maximum power level of an RF signal during a given period. They are useful for assessing high-power signals and ensuring that signal peaks do not exceed safe levels.
Average Power Detectors: Average power detectors measure the mean power level of an RF signal over time. They are commonly used in applications where continuous signal monitoring is required, such as in communication systems.
True RMS Power Detectors: True RMS (Root Mean Square) power detectors provide accurate power measurements of both sine and non-sine waveforms. They are ideal for analyzing complex signals and ensuring precise power measurements.
Digital Power Detectors: Digital RF power detectors offer advanced features such as digital readouts and data logging. They are used in applications requiring high precision and detailed analysis, including laboratory testing and complex signal monitoring.
Each type of RF power detector has unique features suited to different measurement needs, making it important to select the right device based on your specific requirements.
Cell phones themselves cannot directly detect hidden cameras. However, they can be equipped with apps that utilize the phone’s sensors to identify potential surveillance devices. These apps may scan for unusual Wi-Fi networks or Bluetooth signals associated with hidden cameras. Additionally, some phones can utilize their camera features to detect infrared light emitted by certain cameras, which are often invisible to the naked eye. However, relying solely on a cell phone for detection is not foolproof, and specialized devices may be necessary for more accurate detection of hidden cameras.
Yes, there are apps available that claim to help users locate hidden listening devices. These apps typically work by analyzing the surrounding electromagnetic fields and detecting unusual signals or frequencies that may indicate the presence of surveillance equipment. Some apps can scan for unauthorized Wi-Fi networks or Bluetooth devices that might be used for audio surveillance. While these apps can provide some level of detection, their effectiveness can vary. It is advisable to combine app usage with other methods of detection for better results, such as using dedicated RF detectors or professional services.
An RF (Radio Frequency) signal detector is a device used to detect and locate radio frequency emissions. It can identify signals from various devices, including wireless microphones, hidden cameras, and other surveillance equipment that transmit data wirelessly. RF detectors typically scan a range of frequencies, alerting the user when they detect a signal. These detectors can help ensure privacy by identifying potential eavesdropping devices. However, they require some knowledge of RF technology to interpret the results accurately, as many household devices also emit radio frequencies that may trigger alerts.
Various devices can set off an RF detector, including wireless microphones, hidden cameras, and other surveillance equipment that transmit radio signals. Common household items such as Wi-Fi routers, cordless phones, and Bluetooth devices can also trigger alerts due to their radio frequency emissions. Even microwave ovens and certain smart home devices might cause interference. When using an RF detector, it’s essential to distinguish between legitimate threats and benign devices, as everyday electronics can often generate similar signals, leading to false alarms during scans.
To detect RF signals in a house, you can use an RF signal detector, which scans for electromagnetic signals emitted by wireless devices. Start by turning off known electronics to minimize interference, then walk around your home with the detector, paying attention to areas where you suspect hidden devices might be located. You can also utilize apps designed for smartphones that analyze RF signals. For more thorough detection, consider hiring a professional service specializing in counter-surveillance. Regularly inspecting your environment and staying aware of unusual electronic behavior can also aid in detection.
Yes, RF detectors can potentially find hidden cameras, especially if those cameras are wireless and emit radio frequency signals. The detector scans the environment for signals within a specific frequency range that might be associated with surveillance equipment. However, the effectiveness of RF detectors can vary based on the type of camera and its transmission method. Wired cameras, for instance, do not emit RF signals and would not be detected. For the best results, combine RF detection with visual inspections and other detection methods to ensure thorough surveillance detection.


































